 vuex实践使用
vuex实践使用
# 组件通信的几种方式
# 总括
Vue 组件常用几种种的通信方式:
# 数据是单向数据流;
- props /
$emit $parent/$children与refs$attrs/$listeners- provide / inject
- EventBus中央事件总线
- Vuex状态管理
$emit/$on$boradcast和$dispatch
常见使用场景可以分为三类:
- 父子通信:props / $emit;$parent / $children/ ref;$attrs/$listeners;provide / inject API;
- 兄弟通信:eventBus; Vuex
- 跨级通信:
$emit/$on,Vuex;$attrs/$listeners;provide / inject API
详细点:
父子组件通信
父->子
props,子->父$on、$emit获取父子组件实例
$parent、$childrenRef获取实例的方式调用组件的属性或者方法Provide、inject官方不推荐使用,但是写组件库时很常用兄弟组件通信
Event Bus实现跨组件通信Vue.prototype.$bus = new VueVuex跨级组件通信
$attrs、$listeners;<child3 v-bind="$attrs" v-on="$listeners"></child3>Provide、inject 用在组件库中多;Vuex 大型
# EventBus事件
在vue中传递数据是通过属性传递(父子关系),子父通信是通过emit来触发父级事件。如果遇到平级组件可以通过共同的父级进行数据传递。但是在开发中,我们经常会遇到平级组件数据交互和跨组件数据交互就可以通过一个共同的实例来进行数据传递。 通过事件来共享数据(发布订阅模式)
创建bus实例
// lib/bus.js
import Vue from 'vue';
let $bus = new Vue();
Vue.prototype.$bus = $bus;
// main.js
import './lib/bus';
// Boy组件 发射dinner事件
<template>
<div>男孩
<button @click="sayToGirl()">对女孩说话</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
methods: {
sayToGirl(){
this.$bus.$emit('dinner','你饿吗');
}
}
}
</script>
// Girl组件 监听dinner事件
<template>
<div>
女孩 <span>男孩对我说: {{message}}</span>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data(){
return {message:''}
},
mounted() {
this.$bus.$on('dinner',(data)=>{
this.message = data;
})
}
}
</script>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# vuex管理状态
# Vuex的用法实践
vuex是vue的状态管理工具,为了更方便实现多个组件共享状态
# 基础使用
这里我们可以进行类比: SGMA MP
- state 类比为组件的状态 ;
- getters类比为组件的计算属性 ;
- mutations类比为组件中的方法(可以更改组件的状态),使用commit;
- actions用于进行异步操作将结果提交给mutation; 使用dispatch;
其他辅助函数有:
- mapState
- mapGetters
- mapMutations
- mapActions
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
state: {
age: 18
},
getters: {
getAge(state) {
return state.age + 10;
}
},
mutations: {
changeAge(state, payload) {
state.age += payload
}
},
actions: {
changeAge({commit}, payload) {
setTimeout(() => {
commit('changeAge', payload);
}, 1000);
}
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
<div id="app">
我的年龄是: {{this.$store.state.age}}
<br />
年龄是: {{this.$store.getters.getAge}}
<br />
<!-- commit 对应的mutation -->
<button @click="$store.commit('changeAge',5)">立即增加年龄
<!-- dispatch对应的action -->
<button @click="$store.dispatch('changeAge',3)">过一会增加年龄</button>
</button>
</div>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
这个$store属性是通过根实例传入的
new Vue({
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
2
3
4
内部会将store属性挂载在每个实例上命名为$store,这样所有组件都可以操作同一个store属性
# state&getters
mapState,mapGetters
默认模块中的状态都是挂在在对应的模块内,并没有直接放到根状态上。像后面的getters/mutations/actions默认都会合并在根模块中
state类比组件中的状态
// state.js let state = { lesson:'架构' } export default state; // 可以在组件中直接通过 this.$store.state来访问数据,也可以通过计算属性的方式 <template> <div> 课程是:{{lesson}} </div> </template> <script> export default { computed: { lesson(){ return this.$store.state.lesson } } } </script> // vue提供的辅助函数的使用示范 import {mapState} from 'vuex'; export default { computed: { // 直接取出状态中的结果 ...mapState(['lesson']), // 给状态起名字 ...mapState({lesson1:'lesson'}), // 通过函数的方式获取结果 ...mapState({lesson2:state=>state.lesson}) } } // 模块中的状态;模块命名空间的示范 let teacher = { namespaced:true, state:{ name:'samy' } } export default teacher; // 取值时需要通过模块的名字来获取对应的状态 <template> <div> teacherName: {{name}} </div> </template> <script> import {mapState} from 'vuex'; export default { computed: { // 当模块中指定了namespaced:true时 可以使用第一个参数来限定取值的模块 ...mapState({name:state=>state.teacher.name}), ...mapState('teacher',['name']), // state指代的是teacher中的状态 ...mapState('teacher',{teacherName:state=>state.name}) } } </script> // 使用createNamespacedHelpers import {createNamespacedHelpers} from 'vuex'; // 通过createNamespacedHelpers 方法来获取对应的mapstate let {mapState} = createNamespacedHelpers('teacher'); export default { computed: { ...mapState(['name']) } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72getters类比组件中的计算属性
import {mapState,mapGetters} from 'vuex'; <div> {{getLessonName}} </div> export default { computed: { // getName(){ // return this.$store.getters.getLessonName // } ...mapGetters(['getLessonName'])//通过辅助函数可以简写很多; } } // 如果模块中有namespaced:true <template> <div> teacherName: {{getTeacherName}} </div> </template> <script> import {createNamespacedHelpers} from 'vuex'; let {mapState,mapGetters} = createNamespacedHelpers('teacher'); export default { computed: { ...mapGetters(['getTeacherName']) } } </script>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
把模块中的状态进行计算,映射出对应的结果
# mutations&actions
- mutation突变,唯一修改状态的方式
strict:process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' // 严格模式修改状态只能通过mutation来修改
let mutations = {
SET_LESSON_NAME(state,payload){ // 载荷
state.lesson = payload;
// 修改时需要获取对象的属性
// state.lesson = payload.name;
}
}
export default mutations;
// 载在组件中调用commit方法 触发mutation对应的方法
changeName(){
this.$store.commit('SET_LESSON_NAME','node')
// 可以写成对象的方式传递;payload是字符串或者对象;
// this.$store.commit({
// type:'SET_LESSON_NAME',
// name:'node'
// });
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
给状态新增不存在的属性,需要通过Vue.set方法;
Vue.set(state,'number',payload.number);
import {mapState,mapGetters,mapMutations} from 'vuex';
methods: {
...mapMutations(['SET_LESSON_NAME']), //mapMutations简化方法;
...mapMutations({
setNumber:'SET_NUMBER', // 重命名;
}).
//然后调用this.setNumber(10)相当调用this.$store.commit('SET_NUMBER',10)
changeName(){
this['SET_LESSON_NAME']({number:10});
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
mutation不能操作异步逻辑;【规定】;严格模式下会提示;
- actions就是用来处理异步的请求,异步更新状态
// 派发动作到action中
this.$store.dispatch('SET_LESSON_NAME');
// 在action中处理异步逻辑后将结果提交给mutation
import {getLesson} from '../api/lesson'
let actions = {
// 在action中需要将数据提交给mutation,这里可以做异步逻辑
SET_LESSON_NAME({commit},payload){
getLesson().then(data=>{
// data => {name:node}
commit({type:'SET_LESSON_NAME',...data});
})
}
}
export default actions;
// 使用mapActions简化方法;
methods: {
...mapActions(['SET_LESSON_NAME']),
changeName(){
this['SET_LESSON_NAME']();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
action中可以做封装异步请求,多个组件相同的异步处理,可以直接调用action,action中可以多次commit,也可以在action中再次调用action
# 进阶用法插件
subscribe的使用 ;store.subscribe((mutation,state)
# persist插件
自动保存到本地插件; 发布订阅;可自己实现插件功能;挂载到store中的plugins数组上;
// vuex中的store容器
export default (store)=>{
// 用新的状态 替换掉老的状态
store.replaceState(JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('state'))|| store.state);
store.subscribe((mutation,state)=>{ // 订阅每次commit都会触发此函数
localStorage.setItem('state',JSON.stringify(state));
});
}
// 使用插件
import saveLocale from './plugins/saveLocale'
export default new Vuex.Store({
state,
getters,
mutations,
actions,
strict:process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production',
modules:{
teacher
},
plugins:[saveLocale]
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
# logger插件
vuex中自己实现了这个插件;
import deepClone from 'lodash/cloneDeep'
export default (store)=>{
let prevState = deepClone(store.state);
store.subscribe((mutation,state)=>{
console.log('prev',prevState.lesson);
console.log(mutation);
console.log('next',state.lesson);
prevState = deepClone(state);
});
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
vuex双向绑定, 当更新数据时手动提交数据的更改
<input type="text" v-model="teacherName">
computed: {
...mapState('teacher',['name']),
teacherName:{
get(){
return this.name;
},
set(val){
this['SET_TEACHER_NAME'](val);
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# vuex与redux的区别
# 核心概念对比
| Redux 的核心概念 | Vuex 的核心概念 |
|---|---|
| action (同步action ,或借助 中间件 实现异步操作,action 不会改变 store,只是描述了怎么改变store) | mutation(用于同步操作) 、action(可用于异步操作,提交 mutation) |
| reducer(纯函数,根据 action 和旧的 store 计算出新的 store | mutation里面直接修改 state |
| store(单一数据源) | state(单一数据源) |
# 工作流向
vuex的流向:
- view——>commit——>mutations——>state变化——>view变化(同步操作)
- view——>dispatch——>actions——>mutations——>state变化——>view变化(异步操作)
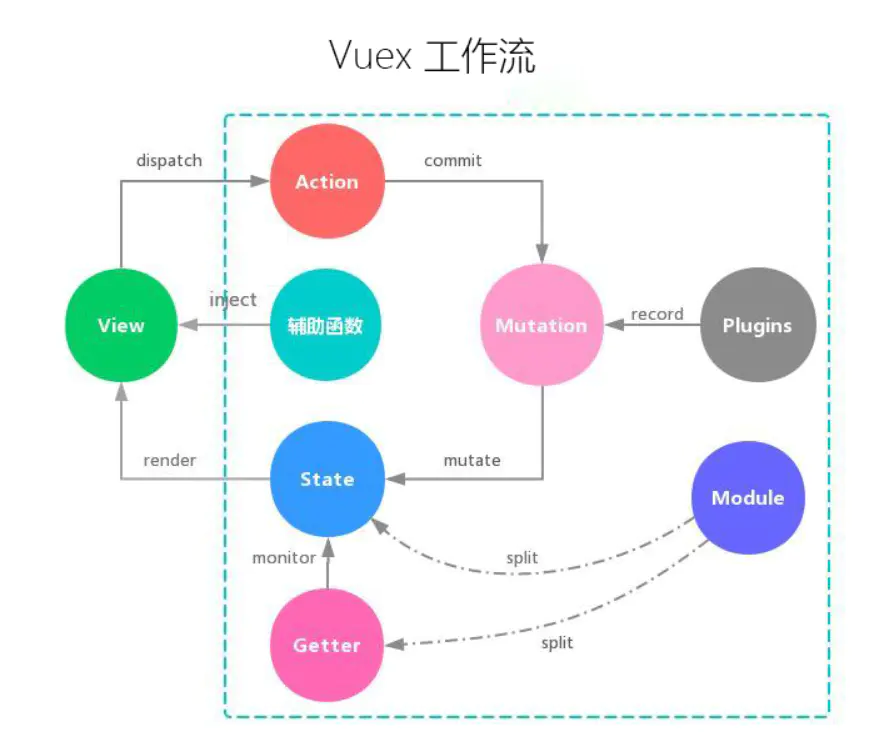
redux的流向: view——>dispatch——>actions——>reducer——>state变化——>view变化(同步异步一样)
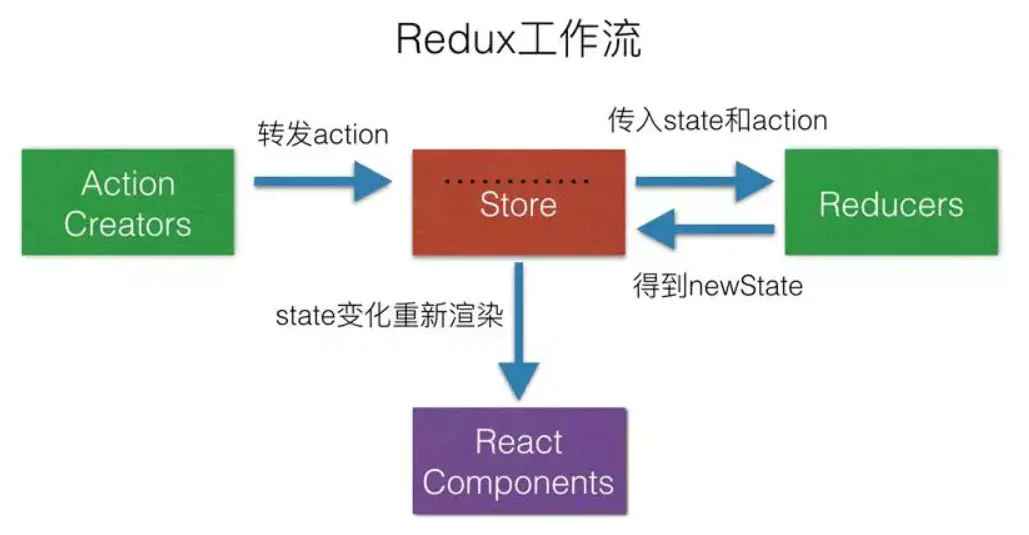
# 不同点
- vuex以mutations函数取代redux中的reducer,只需在对应的mutation函数里改变state即可。
- vuex中的state直接关联到组件实例上,当state变化时自动重新渲染,无需订阅重新渲染函数。redux使用store对象存储整个应用的状态,状态变化时,从最顶层向下传递,每一级都会进行状态比较,从而达到更新。
- vuex支持action异步处理,redux中只支持同步处理,对于异步处理需要借助于redux-thunk和redux-saga实现。
# 使用原则
Redux 的三大原则:
(1)单一数据源(一个Redux应用只有一个store),也是单向的数据流;
(2)state只读(唯一改变 state 的方法就是触发 action,action 是一个用于描述已发生事件的普通对象。);
(3)使用纯函数(reducer)来修改state。
2
3
Vuex 的三大原则:
a. 应用层级的状态应该集中到单个 store 对象中。
b. 提交 mutation 是更改状态的唯一方法,并且这个过程是同步的。
c. 异步逻辑都应该封装到 action 里面。
2
3
