 vue-router自定义实现
vue-router自定义实现
# 简介
实现简版vue-router
路由:不同的路径渲染不同的组件;
什么是路由? 路由就是匹配到对应路径显示对应的组件!
# 基本用法
通过Vue路由的基本配置来探索Vue-Router
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Home from './views/Home.vue'
import About from './views/About.vue'
Vue.use(Router);// 使用Vue-Router插件
// 创建Vue-router实例,将实例注入到main.js中
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
component: About,
children: [
{
path: 'a', component: { //这里二级路由的写法;不能有/;
render(h) {return <h1>about A</h1>}
}
},
{
path: 'b', component: {
render(h) {return <h1>about B</h1>}
}
}
]
}
]
})
new Vue({
router, // 在根实例中注入router实例
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
//封装下的处理方式
//export default new Router({
// mode: 'history', // 不使用#方式
// base: process.env.BASE_URL,
// routes
//});
// 当导航变化时 会依次执行这两个方法
router.beforeEach((from, to, next) => {
console.log(1);
setTimeout(() => {
next();
}, 1000);
});
router.beforeEach((from, to, next) => {
console.log(2);
setTimeout(() => {
next();
}, 1000);
});
export default router;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
发现核心方法:就是Vue.use(Router),在就是new Router产生router实例
# 安装环境
直接借助 cli-service-global, 没有通过脚手架创建项目启动;
开发写demo推荐用这种方式;便捷简单处理;
npm install @vue/cli -g
npm install -g @vue/cli-service-global
vue serve #直接启动项目
2
3
# 编写Vue-Router
自己来实现一个Vue-router插件,这里先来标注一下整体目录结构:
├─vue-router
│ ├─components # 存放vue-router的两个核心组件
│ │ ├─link.js
│ │ └─view.js
│ ├─history # 存放浏览器跳转相关逻辑
│ │ ├─base.js
│ │ └─hash.js
│ ├─create-matcher.js # 创建匹配器
│ ├─create-route-map.js # 创建路由映射表
│ ├─index.js # 引用时的入口文件
│ ├─install.js # install方法
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
默认引用Vue-Router使用的是index.js文件,use方法默认会调用当前返回对象的install方法
import install from './install'
export default class VueRouter{}
VueRouter.install = install; // 提供的install方法
2
3
# 编写install方法
使用这个插件内部会提供:
两个原型上的属性
$router,$route;this._router = options.router;Vue.util.defineReactive(this, "_route", this._router.history.current);两个全局组件
router-link,router-view;
注意这里要做响应式的处理;当current变化后 更新_route属性_
import Link from "./components/link";
import View from "./components/view";
export let _Vue;
export default function install(Vue, options) {
_Vue = Vue;
Vue.mixin({
// 给所有组件都混入一个属性$router $route _route
beforeCreate() {
// 无论是父组件还是子组件 都可以通过 this._routerRoot._router 获取共同的实例
const options = this.$options;
if (options.router) {
this._routerRoot = this; // this指向的是当前组件的实例;给当前根组件增加一个属性_routerRoot代表的是他自己
this._router = options.router;
this._router.init(this); // this就是根实例; mixin调用初始化;初始化监听相关;
// 获取到current属性 将current属性定义在_route上
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, "_route", this._router.history.current);
// _route是响应式的; 当current变化后 更新_route属性; 如果current中的path或者matched的其他属性变化 也是响应式的
} else {
this._routerRoot = this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot; // 组件渲染;是一层层的渲染
}
},
});
// 两个原型上的属性 $router $route; // 仅仅是为了更加方便
// 代表路由中所有的属性;重命名内部中的_routerRoute的_route, _router
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, "$router", {
get() {
return this._routerRoot._router; // 方法 push go repace..
},
});
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, "$route", {
get() {
return this._routerRoot._route; // path matched
},
});
// 插件一般用于定义全局组件 全局指令 过滤器 原型方法....
// 两个全局组件router-link router-view;
Vue.component("router-link", Link);
Vue.component("router-view", View);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
ps:vue.min的原理
Vue-Router 安装最重要的一步就是利用 Vue.mixin 去把 beforeCreate 和 destroyed 钩子函数注入到每一个组件中。Vue.mixin 的定义,在 vue/src/core/global-api/mixin.js 中:
export function initMixin (Vue: GlobalAPI) {
Vue.mixin = function (mixin: Object) {
this.options = mergeOptions(this.options, mixin)
return this
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
它的实现实际上非常简单,就是把要混入的对象通过 mergeOptions 合并到 Vue 的 options 中,由于每个组件的构造函数都会在 extend 阶段合并 Vue.options 到自身的 options 中,所以也就相当于每个组件都定义了 mixin 定义的选项。
在Vue-Router上增加一个init方法,主要目的初始化监听相关及默认第一次跳转;
matcher内部有match & addRoutes,方便后面路由跳转路由匹配及动态添加路由;
import createMatcher from './create-matcher'
import install from './install'
export default class VueRouter{
constructor(options){
// 根据用户传递的routes创建匹配关系,this.matcher需要提供两个方法
// match:match方法用来匹配规则
// addRoutes:用来动态添加路由
this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes || []);
}
init(app){}
}
VueRouter.install = install;
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
ps:vue插件的原理:
Vue 提供了 Vue.use 的全局 API 来注册这些插件,所以我们先来分析一下它的实现原理,定义在 vue/src/core/global-api/use.js 中:
export function initUse(Vue: GlobalAPI) {
Vue.use = function (plugin: Function | Object) {
// 1.如果安装过这个插件直接跳出
const installedPlugins = (this._installedPlugins || (this._installedPlugins = []))
if (installedPlugins.indexOf(plugin) > -1) {
return this
}
// additional parameters
// 2.获取参数并在参数中增加Vue的构造函数
const args = toArray(arguments, 1) //取参数
args.unshift(this)//[this,{a:1,b:2}]
// 3.执行install方法
if (typeof plugin.install === 'function') {
plugin.install.apply(plugin, args)
} else if (typeof plugin === 'function') {
plugin.apply(null, args)
}
// 4.记录安装的插件
installedPlugins.push(plugin)
return this
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
Vue.use 接受一个 plugin 参数,并且维护了一个 _installedPlugins 数组,它存储所有注册过的 plugin;接着又会判断 plugin 有没有定义 install 方法,如果有的话则调用该方法,并且该方法执行的第一个参数是 Vue;最后把 plugin 存储到 installedPlugins 中。
可以看到 Vue 提供的插件注册机制很简单,每个插件都需要实现一个静态的 install 方法,当我们执行 Vue.use 注册插件的时候,就会执行这个 install 方法,并且在这个 install 方法的第一个参数我们可以拿到 Vue 对象,这样的好处就是作为插件的编写方不需要再额外去import Vue ,保存vue版本一致。
# 编写createMatcher方法
把外部传递过来的router树结构,扁平化为对象map方式,方便获取;根据用户的配置和当前请求的路径 渲染对应的组件;
创建匹配器可用用于后续的匹配操作; 用户没有传递配置就默认传入一个空数组
- match通过路由来匹配组件;====》 createMatcher
- addRoutes 动态添加匹配规则;
export default function createMatcher(routes) {
let { pathMap, pathList } = createRouteMap(routes); // 扁平化配置; 根据用户的配置创建一个映射表
// console.log("-----createMatcher-----pathMap-----", pathMap); //pathMap = {'/':Home,'/about':About,'/about/a':'aboutA','/about/b':'aboutB'}
// console.log("-----createMatcher-----pathList-----", pathList);// ["/", "/about", "/about/a", "/about/b"]
function match(location) {
let record = pathMap[location]; // 可能一个路径有多个记录
if (record) {
return createRoute(record, {
path: location,
});
}
// 这个记录可能没有; {path:/,matched:[{},{}]}
return createRoute(null, {
path: location,
});
}
function addRoutes(routes) {
createRouteMap(routes, pathMap, pathList);
}
return {
match, // 用于匹配路径
addRoutes, // 添加路由,用于动态添加路由
};
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
这里需要创建映射关系,需要createRouteMap方法
# 编写createRouteMap方法
// 先序深度; 将当前路由存储到pathList和pathMap中
// pathMap = {路径:记录}
function addRouteRecord(route, pathMap, pathList, parent) {
// 当访问/ 时 应该渲染home组件 / => {Home}
// 要判断 儿子的路径不是以 /开头的否则不拼接 父路径
let path = parent ? parent.path + "/" + route.path : route.path;
// 提取需要的信息
let record = {
path,
parent, // parent指代的就是父记录
component: route.component,
name: route.name, //其他相关
props: route.props,
params: route.params || {},
meta: route.meta,
};
// 不能定义重复的路由 否则值生效最后一个
if (!pathMap[path]) {
pathMap[path] = record;
pathList.push(path);
}
if (route.children) {
route.children.forEach((childRoute) => {
// addRouteRecord(childRoute, pathMap, pathList, route); // 在遍历儿子时 将父亲的记录传入进去
addRouteRecord(childRoute, pathMap, pathList, record); // 在遍历儿子时 将父亲的记录传入进去
});
}
}
export default function createRouteMap(routes, oldPathMap, oldPathList) {
// 当第一次加载的时候没有pathMap和pathList
// let pathMap = oldPathMap || {}; // 1个参数时初始化 2个参数就是动态添加路由
let pathMap = oldPathMap || Object.create(null); // 默认没有传递就是直接创建映射关系
let pathList = oldPathList || [];
routes.forEach((route) => {
addRouteRecord(route, pathMap, pathList);
});
return {
pathMap,
pathList,
};
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
该方法主要是处理路径和不同路径对应的记录
matcher我们先写到这,稍后在来补全match方法的实现
# 编写浏览器历史相关代码
# 核心逻辑current【要点】
最终核心 需要将current属性变化成响应式的 后续current变化会更新视图
在构造时,获取current;
在base.js中; this.current = {path:'/',matched:[]}
constructor(router) {
this.router = router;
this.cb = null;
// 当我们创建完路由后 ,先有一个默认值 路径 和 匹配到的记录做成一个映射表
// 默认当创建history时 路径应该是/ 并且匹配到的记录是[]
this.current = createRoute(null, {
path: "/", // 存放路由状态的
});
// /about/a => [/about /about/a]
// this.current = {path:'/',matched:[]}
console.log(this.current);
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 在router初始化逻辑
init(app) {
const history = this.history;
// hash的特色处理; 监听hash值变化 默认跳转到对应的路径中; 切片编程
const setupHashListener = () => {
history.setupListener(); // 监听路由变化hashchange;hash的特殊性
};
// 初始化会先获得当前hash值进行跳转, 并且监听hash变化
history.transitionTo(
history.getCurrentLocation(), // 获取当前的位置
setupHashListener
);
// 改变了 响应式数据
history.listen((route) => {
app._route = route; // 每次路径变化都会调用此方法;【订阅】
});
// setupListener 放到hash里取
// transitionTo 放到base中 做成公共的方法
// getCurrentLocation // 放到自己家里 window.location.hash / window.location.pathname
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
这里要分别实现 transitionTo(基类方法)、 getCurrentLocation 、setupListener
getCurrentLocation实现
function getHash(){
return window.location.hash.slice(1);
//return window.location.pathname;
}
export default class HashHistory extends History{
// ...
getCurrentLocation(){
return getHash();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
setupListener实现
export default class HashHistory extends History{
// ...
setupListener(){
window.addEventListener('hashchange', ()=> {
this.transitionTo(getHash());
})
// window.addEventListener("popstate", () => {
// this.transitionTo(this.getCurrentLocation());
//});
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
可以看到最核心的还是transitionTo方法
TransitionTo实现【要点】
通过path找到route信息,再处理路由监听,再回调出去页面加载;
export function createRoute(record, location) { // {path:'/',matched:[record,record]}
let res = [];
if (record) { // 如果有记录
while(record){
res.unshift(record); // 就将当前记录的父亲放到前面
record = record.parent
}
}
return {
...location,
matched: res
}
}
export default class History {
constructor(router) {
this.router = router;
// 根据记录和路径返回对象,稍后会用于router-view的匹配
this.current = createRoute(null, {
path: '/'
})
}
// 核心逻辑
transitionTo(location, onComplete) {
// 去匹配路径
let route = this.router.match(location);
if(
location === route.path &&
route.matched.length === this.current.matched.length){
return
}
this.updateRoute(route); // 更新路由即可
onComplete && onComplete();
}
updateRoute(route){ // 跟新current属性
this.current =route;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
export default class VueRouter{
// ...
match(location){
return this.matcher.match(location);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
终于这回可以完善一下刚才没有写完的match方法
function match(location){ // 稍后根据路径找到对应的记录
let record = pathMap[location]
if (record) { // 根据记录创建对应的路由
return createRoute(record,{
path:location
})
}
// 找不到则返回空匹配
return createRoute(null, {
path: location
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
不难发现路径变化时都会更改current属性,可以把current属性变成响应式的,每次current变化刷新视图即可
export let _Vue;
export default function install(Vue) {
_Vue = Vue;
Vue.mixin({ // 给所有组件的生命周期都增加beforeCreate方法
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options.router) { // 如果有router属性说明是根实例
// ...
Vue.util.defineReactive(this,'_route',this._router.history.current);
}
// ...
}
});
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
Vue.util.defineReactive 这个方法是vue中响应式数据变化的核心
当路径变化时需要执行此回调更新_route属性, 在init方法中增加监听函数
history.listen((route) => { // 需要更新_route属性
app._route = route
});
2
3
export default class History {
constructor(router) {
this.cb = null;
}
listen(cb){
this.cb = cb; // 注册函数
}
updateRoute(route){
this.current =route;
this.cb && this.cb(route); // 更新current后 更新_route属性
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
# 两种模式比较
- hash默认时,要匹配/路由;
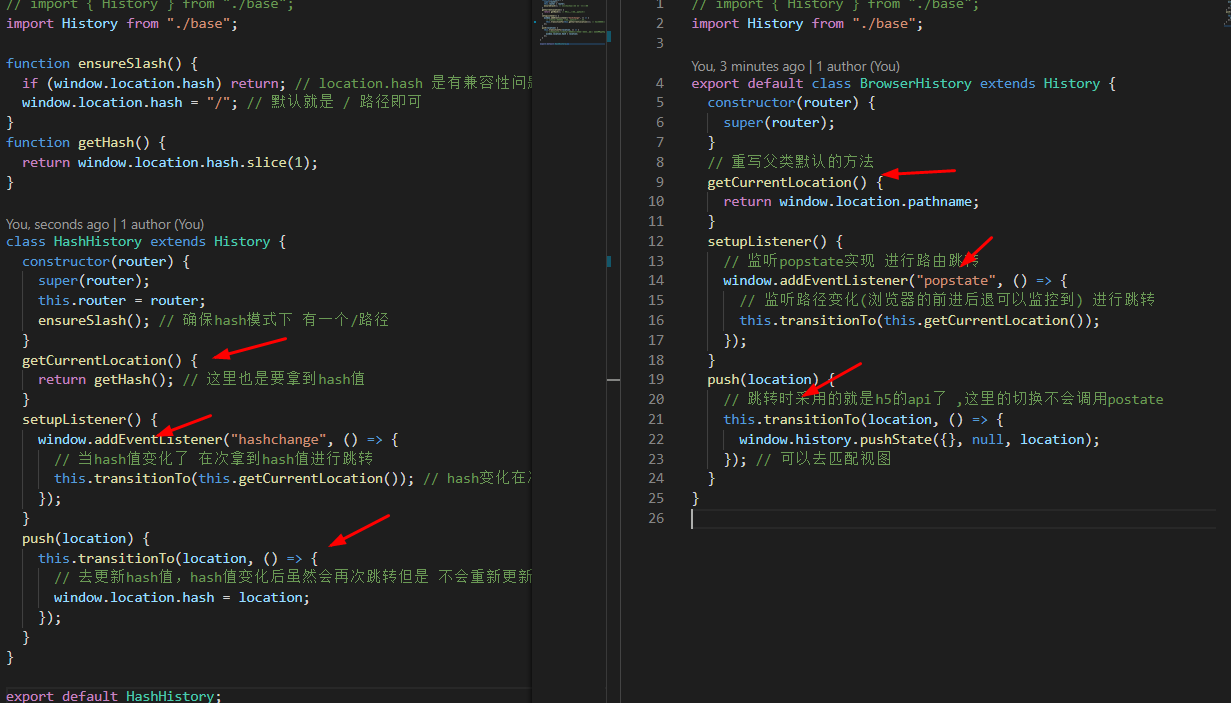
import HashHistory from './history/hash'
constructor(options){
this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes || []);
// vue路由有三种模式 hash / h5api /abstract ,为了保证调用时方法一致。我们需要提供一个base类,在分别实现子类,不同模式下通过父类调用对应子类的方法
this.history = new HashHistory(this);
}
2
3
4
5
6
这里我们以hash路由为主,创建hash路由实例
import History from './base'
// hash路由
export default class HashHistory extends History{
constructor(router){
super(router);
}
}
// 路由的基类
export default class History {
constructor(router){
this.router = router;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
如果是hash路由,打开网站如果没有hash默认应该添加#/
import History from './base';
function ensureSlash(){
if(window.location.hash){
return
}
window.location.hash = '/'
}
export default class HashHistory extends History{
constructor(router){
super(router);
ensureSlash(); // 确保有hash
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 编写Link及View组件
# router-link组件
默认是<a>,绑定事件处理;再用jsx方便组件库封装;
export default {
name: "routerLink",
props:{
to:{
type:String,
required:true
},
tag:{
type:String
}
},
render(h){
let tag = this.tag || 'a';
let handler = ()=>{
this.$router.push(this.to);
}
return <tag onClick={handler}>{this.$slots.default}</tag>
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
# router-view组件
要考虑路由嵌套,叠加处理;用 【函数式组件】编写;
函数式组件的特点: 性能高,不用创建实例 = react函数组件 new Ctor().$mount()
理解$vnode与_vnode的区别:
$vnode代表的是占位符vnode 组件的标签名的虚拟节点_vnode代表的是组件内部渲染的虚拟节点;
要点:parent.$vnode && parent.$vnode.data.routerView
官方文档:render: function (createElement, context)组件需要的一切都是通过 context 参数传递,它是一个包括如下字段的对象:
props:提供所有 prop 的对象children:VNode 子节点的数组slots:一个函数,返回了包含所有插槽的对象scopedSlots:(2.6.0+) 一个暴露传入的作用域插槽的对象。也以函数形式暴露普通插槽。data:传递给组件的整个数据对象 (opens new window),作为createElement的第二个参数传入组件parent:对父组件的引用listeners:(2.3.0+) 一个包含了所有父组件为当前组件注册的事件监听器的对象。这是data.on的一个别名。injections:(2.3.0+) 如果使用了inject(opens new window) 选项,则该对象包含了应当被注入的 property。
export default {
name: "routerView",
functional:true,
render(h,{parent,data}){
let route = parent.$route;
let depth = 0;
data.routerView = true;
while(parent){ // 根据matched 渲染对应的router-view
if (parent.$vnode && parent.$vnode.data.routerView){
depth++;
}
parent = parent.$parent;
}
let record = route.matched[depth];
if(!record){
return h();
}
return h(record.component, data);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
# install初始化挂载
import Link from "./components/link";
import View from "./components/view";
// 插件一般用于定义全局组件 全局指令 过滤器 原型方法....
// 两个全局组件router-link router-view;
Vue.component("router-link", Link);
Vue.component("router-view", View);
2
3
4
5
6
7
# 路由守卫实现
# 路由分类
a. 全局守卫
beforeEach— 全局前置钩子(每个路由调用前都会触发,根据 from 和 to 来判断是哪个路由触发)beforeResolve— 全局解析钩子(和 router.beforeEach 类似,区别是在导航被确认之前,同时在所有组件内守卫和异步路由组件被解析之后,解析守卫就被调用)afterEach— 全局后置钩子
b. 路由独享守卫
beforeEnter— 路由配置上可以直接定义beforeEnter守卫。
c. 组件内守卫
beforeRouteEnter— 在渲染该组件的对应路由被 confirm 前调用,不能获取组件实例this,因为当守卫执行前,组件实例还没被创建。beforeRouteUpdate— 当前路由改变,但是该组件被复用时调用beforeRouteLeave— 导航离开该组件的对应路由时调用
# 完整的导航解析流程
- 导航被触发。
- 在失活的组件里调用
beforeRouteLeave守卫。 - 调用全局的
beforeEach守卫。 - 在重用的组件里调用
beforeRouteUpdate守卫 (2.2+)。 - 在路由配置里调用
beforeEnter。 - 解析异步路由组件。
- 在被激活的组件里调用
beforeRouteEnter。 - 调用全局的
beforeResolve守卫 (2.5+)。 - 导航被确认。
- 调用全局的
afterEach钩子。 - 触发 DOM 更新。
- 调用
beforeRouteEnter守卫中传给next的回调函数,创建好的组件实例会作为回调函数的参数传入。
# beforeEach实现
导航守卫 核心就是把所有方法 组合成一个数组 依次调用
this.beforeHooks = [];
beforeEach(fn){ // 将fn注册到队列中
this.beforeHooks.push(fn);
}
2
3
4
# 中间件逻辑
在跳转时处理;将用户函数注册到数组中
function runQueue(queue, iterator,cb) { // 迭代queue
function step(index){
if(index >= queue.length){
cb();
}else{
let hook = queue[index];
// 将本次迭代到的hook 传递给iterator函数中,将下次的权限也一并传入
iterator(hook,()=>{
step(index+1)
})
}
}
step(0)
}
export default class History {
transitionTo(location, onComplete) {
// 跳转到这个路径
let route = this.router.match(location);
if (location === this.current.path && route.matched.length === this.current.matched.length) {
return
}
let queue = [].concat(this.router.beforeHooks);
const iterator = (hook, next) => {
hook(route,this.current,()=>{ // 分别对应用户 from,to,next参数
next();
});
}
runQueue(queue, iterator, () => { // 依次执行队列 ,执行完毕后更新路由
this.updateRoute(route);
onComplete && onComplete();
});
}
updateRoute(route) {
this.current = route;
this.cb && this.cb(route);
}
listen(cb) {
this.cb = cb;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
# 总括
核心:
- 理解
Vue.use和Vue.mixin的原理; - 两个原型上的属性
$route,$router; - 两个全局组件
router-link,router-view; - 需要将current属性变化成响应式的,后续current变化更新视图;
create-matcher暴露了match,addRoutes两个方法;- 导航守卫 核心就是把所有方法 组合成一个数组 依次调用; 跟koa中的洋葱模型类似;
