 dva使用实践
dva使用实践
# 简介
dva 首先是一个基于 redux (opens new window) 和 redux-saga (opens new window) 的数据流方案,然后为了简化开发体验,dva 还额外内置了 react-router (opens new window) 和 fetch (opens new window),所以也可以理解为一个轻量级的应用框架。
- 基于
redux、redux-saga和react-router的轻量级前端框架。(Inspired by elm and choo) - dva是基于react+redux最佳实践上实现的封装方案,简化了redux和redux-saga使用上的诸多繁琐操作
# 特性
- 易学易用,仅有 6 个 api,对 redux 用户尤其友好,配合 umi 使用 (opens new window)后更是降低为 0 API
- elm 概念,通过 reducers, effects 和 subscriptions 组织 model
- 插件机制,比如 dva-loading (opens new window) 可以自动处理 loading 状态,不用一遍遍地写 showLoading 和 hideLoading
- 支持 HMR,基于 babel-plugin-dva-hmr (opens new window) 实现 components、routes 和 models 的 HMR
# 数据流向
- 数据的改变发生通常是通过:
- 用户交互行为(用户点击按钮等)
- 浏览器行为(如路由跳转等)触发的
- 当此类行为会改变数据的时候可以通过 dispatch 发起一个 action,如果是同步行为会直接通过 Reducers 改变 State ,如果是异步行为(副作用)会先触发 Effects 然后流向 Reducers 最终改变 State
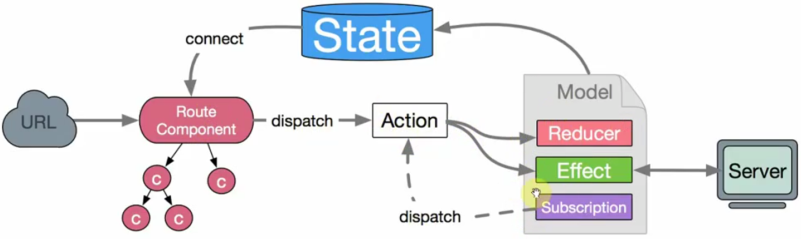
# 8个概念
# 1. dispatch函数
dispatching function 是一个用于触发 action 的函数
action 是改变 State 的唯一途径,但是它只描述了一个行为,而 dipatch 可以看作是触发这个行为的方式,而 Reducer 则是描述如何改变数据的。
在 dva 中,connect Model 的组件通过 props 可以访问到 dispatch,可以调用 Model 中的 Reducer 或者 Effects,常见的形式如:
dispatch({ type: 'user/add', // 如果在 model 外调用,需要添加 namespace payload: {}, // 需要传递的信息 });1
2
3
4
# 2. Action
- Action 是一个普通 javascript 对象,它是改变 State 的唯一途径。
- 无论是从 UI 事件、网络回调,还是 WebSocket 等数据源所获得的数据,最终都会通过 dispatch 函数调用一个 action,从而改变对应的数据。
- action 必须带有 type 属性指明具体的行为,其它字段可以自定义,
- 如果要发起一个 action 需要使用 dispatch 函数;
- 需要注意的是 dispatch 是在组件 connect Models以后,通过 props 传入的。
# 3. State
- State 表示 Model 的状态数据,通常表现为一个 javascript 对象(当然它可以是任何值);
- 操作的时候每次都要当作不可变数据(immutable data)来对待,保证每次都是全新对象,没有引用关系,这样才能保证 State 的独立性,便于测试和追踪变化。
# 4. Reducer
- Reducer(也称为 reducing function)函数接受两个参数:之前已经累积运算的结果和当前要被累积的值,返回的是一个新的累积结果。该函数把一个集合归并成一个单值。
- 在 dva 中,reducers 聚合积累的结果是当前 model 的 state 对象。
- 通过 actions 中传入的值,与当前 reducers 中的值进行运算获得新的值(也就是新的 state)。
- 需要注意的是 Reducer 必须是纯函数,所以同样的输入必然得到同样的输出,它们不应该产生任何副作用。
- 并且,每一次的计算都应该使用immutable data,这种特性简单理解就是每次操作都是返回一个全新的数据(独立,纯净),所以热重载和时间旅行这些功能才能够使用。
# 5. Effect
- Effect 被称为副作用,在我们的应用中,最常见的就是异步操作。
- 它来自于函数编程的概念,之所以叫副作用是因为它使得我们的函数变得不纯,同样的输入不一定获得同样的输出。
- dva 为了控制副作用的操作,底层引入了redux-sagas做异步流程控制,由于采用了generator的相关概念,所以将异步转成同步写法,从而将effects转为纯函数。
# 6. Subscription
Subscriptions 是一种从 源 获取数据的方法,它来自于 elm。
Subscription 语义是订阅,用于订阅一个数据源,然后根据条件 dispatch 需要的 action
数据源可以是当前的时间、服务器的 websocket 连接、keyboard 输入、geolocation 变化、history 路由变化等等。
import key from 'keymaster'; ... app.model({ namespace: 'count', subscriptions: { keyEvent({dispatch}) { key('⌘+up, ctrl+up', () => { dispatch({type:'add'}) }); }, } });1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
# 7. Router
这里的路由通常指的是前端路由
由于我们的应用现在通常是单页应用,所以需要前端代码来控制路由逻辑
通过浏览器提供的 History API 可以监听浏览器url的变化,从而控制路由相关操作。
dva 实例提供了 router 方法来控制路由,使用的是react-router (opens new window)。
import { Router, Route } from 'dva/router'; app.router(({history}) => <Router history={history}> <Route path="/" component={HomePage} /> </Router> );1
2
3
4
5
6
# 8. Route Components
- 在组件设计方法中,我们提到过 Container Components,在 dva 中我们通常将其约束为 Route Components
- 因为在 dva 中我们通常以页面维度来设计 Container Components。
- 所以在 dva 中,通常需要 connect Model的组件都是 Route Components,组织在/routes/目录下,而/components/目录下则是纯组件(Presentational Components)。
# 实践
# 初始化环境
create-react-app demo
cd demo
npm i -S dva redux react-redux react-saga react-router-dom react-router-redux history
2
3
# 文件结构
官方推荐的:
├── /mock/ # 数据mock的接口文件
├── /src/ # 项目源码目录
│ ├── /components/ # 项目组件
│ ├── /routes/ # 路由组件(页面维度)
│ ├── /models/ # 数据模型
│ ├── /services/ # 数据接口
│ ├── /utils/ # 工具函数
│ ├── route.js # 路由配置
│ ├── index.js # 入口文件
│ ├── index.less
│ └── index.html
├── package.json # 定义依赖的pkg文件
└── proxy.config.js # 数据mock配置文件
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
# 计数器示例
| 用法 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| app = dva(opts) | 创建应用,返回 dva 实例 |
| app.use(hooks) | 配置 hooks 或者注册插件 |
| app.model(model) | 注册 model |
| app.router(({ history, app }) => RouterConfig) | 注册路由表 |
| app.start(selector?) | 启动应用。selector 可选 |
- namespace model 的命名空间,同时也是他在全局 state 上的属性,只能用字符串
- state 初始值
- reducers 以 key/value 格式定义 reducer。用于处理同步操作,唯一可以修改 state 的地方。由 action 触发。
- effects 以 key/value 格式定义 effect。用于处理异步操作和业务逻辑,不直接修改 state。由 action 触发,可以触发 action,可以和服务器交互,可以获取全局 state 的数据等等。
- subscriptions 以 key/value 格式定义 subscription。subscription 是订阅,用于订阅一个数据源,然后根据需要 dispatch 相应的 action。在 app.start() 时被执行,数据源可以是当前的时间、服务器的 websocket 连接、keyboard 输入、geolocation 变化、history 路由变化等等。
import React from 'react';
import dva, { connect } from 'dva'
// 1. Initialize
const app = dva()
// 2. Plugins
// app.use({});
// 3. Model
// app.model(require('./models/example').default);
app.model({
namespace: 'counter',
state: { number: 0 },
reducers: {
//接收老状态,返回新状态
add(state) {
//dispatch({type:'add'});
return { number: state.number + 1 }
},
minus(state) {
//dispatch({type:'minus'})
return { number: state.number - 1 }
}
}
})
const Counter = connect(state => state.counter)(props => (
<div>
<p>{props.number}</p>
<button onClick={() => props.dispatch({ type: 'counter/add' })}>+</button>
<button onClick={() => props.dispatch({ type: 'counter/minus' })}>-</button>
</div>
))
// 4. Router
// app.router(require('./router').default);
app.router(() => <Counter />)
// 5. Start
app.start('#root')
// ReactROM.render(() => <Counter />, document.querySelector('#root'))
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
TS版本
import React from 'react';
import { Dispatch } from 'redux';
import dva, { connect } from 'dva';
import keymaster from 'keymaster';
import { RouterAPI } from 'dva';
import { Router, Route } from 'dva/router';
interface Counter1State {
number: 0
}
interface Counter2State {
number: 0
}
interface CombinedState {
counter1: Counter1State;
counter2: Counter2State;
}
const app = dva();
const delay = (millseconds: number) => {
return new Promise(function (resolve, reject) {
setTimeout(function () {
resolve();
}, millseconds);
});
}
app.model({
namespace: 'counter1',
state: { number: 0 },
reducers: {//接收老状态,返回新状态
add(state) { //dispatch({type:'add'});
return { number: state.number + 1 };
},
minus(state) {//dispatch({type:'minus'})
return { number: state.number - 1 };
}
},
effects: {// 延时操作 调用接口 等待
*asyncAdd(action, { put, call }) { //redux-saga/effects {put,call}
yield call(delay, 1000);//把100传给delay并调用,yield会等待promise完成
yield put({ type: 'add' });
}
},
subscriptions: {
keyboard({ dispatch }) {
keymaster('space', () => {
dispatch({ type: 'add' });
});
},
changeTitle({ history }) {
setTimeout(function () {
history.listen(({ pathname }) => {
document.title = pathname;
});
}, 1000);
}
}
});
app.model({
namespace: 'counter2',
state: { number: 0 },
reducers: {//接收老状态,返回新状态
add(state) { //dispatch({type:'add'});
return { number: state.number + 1 };
},
minus(state) {//dispatch({type:'minus'})
return { number: state.number - 1 };
}
}
});
type Counter1Props = Counter1State & { dispatch: Dispatch };
const Counter1 = (props: Counter1Props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>{props.number}</p>
<button onClick={() => props.dispatch({ type: 'counter1/add' })}>add</button>
<button onClick={() => props.dispatch({ type: 'counter1/asyncAdd' })}>asyncAdd</button>
<button onClick={() => props.dispatch({ type: 'counter1/minus' })}>-</button>
</div>
)
}
type Counter2Props = Counter2State & { dispatch: Dispatch };
const Counter2 = (props: Counter2Props) => {
return (
<div>
<p>{props.number}</p>
<button onClick={() => props.dispatch({ type: 'counter2/add' })}>+</button>
<button onClick={() => props.dispatch({ type: 'counter2/minus' })}>-</button>
</div>
)
}
const mapStateToProps1 = (state: CombinedState): Counter1State => state.counter1;
const ConnectedCounter = connect(
mapStateToProps1
)(Counter1);
const mapStateToProps2 = (state: CombinedState): Counter2State => state.counter2;
const ConnectedCounter2 = connect(
mapStateToProps2
)(Counter2);
app.router(
(api?: RouterAPI) => {
let { history } = api!;
return (
(
<Router history={history}>
<>
<Route path="/counter1" component={ConnectedCounter} />
<Route path="/counter2" component={ConnectedCounter2} />
</>
</Router>
)
)
}
);
app.start('#root');
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
- namespace model 的命名空间,同时也是他在全局 state 上的属性,只能用字符串
- state 初始值
- reducers 以 key/value 格式定义 reducer。用于处理同步操作,唯一可以修改 state 的地方。由 action 触发。
- effects 以 key/value 格式定义 effect。用于处理异步操作和业务逻辑,不直接修改 state。由 action 触发,可以触发 action,可以和服务器交互,可以获取全局 state 的数据等等。
- subscriptions 以 key/value 格式定义 subscription。subscription 是订阅,用于订阅一个数据源,然后根据需要 dispatch 相应的 action。在 app.start() 时被执行,数据源可以是当前的时间、服务器的 websocket 连接、keyboard 输入、geolocation 变化、history 路由变化等等。
# 相关链接
https://dvajs.com/
https://dvajs.com/guide/source-code-explore.html
