 vue-cli源码分析
vue-cli源码分析
# 前言
# 发布
Evan You (opens new window) 8月10日 在 Medium (opens new window)发布了 Vue CLI 3.0 is here! (opens new window),这标志着 vue-cli 进入了 3.0 时代。从这以后,vue 开发体验更加地优秀,开发逼格更加地高大。
其实,不是这样的,事实是:从这以后,你要明白,你又要继续学习了,尤大,你尽管更新,我们还学得动。
# 版本
vue-cli 从 3.0.0-alpha.1 到 3.0.0 一共发布了 41 个版本,其中包括 13 个 alpha 版本,16 个 beta 版本以及 12 个 rc 版本,本次源码采用的版本是 3.1.3,也是在写这篇文章时的最新版本。截止 3.1.3,npm 上一共发布了 51 个版本。所以: 一个好的项目不是一次写成的,只有不断地 fix bugs 才能更加完善 。
vue-cli npm versions (opens new window)

# 仓库
Github 仓库 : vue-cli (opens new window)
仓库默认分支为 dev, 这个分支下放着vue-cli3.0 以及与之配套的一些插件代码,master 分支为 vue-cli 2.X.X 的代码。其中 vue-cli 的源码在 /packages/@vue/cli 中,看这目录的格式,应该是尤大将工具以及vue-cli 的一些插件都归在了 npm @vue 的组织下面,npm @vue (opens new window)。
# 开始
# 环境介绍
# 版本
- @vue/cli: 3.1.3
- @vue/cli-service: 3.1.4
- node:8.11.4
- platform: macOS
# 工具
- vscode: 代码编辑器
- Typora: Markdown 编辑器
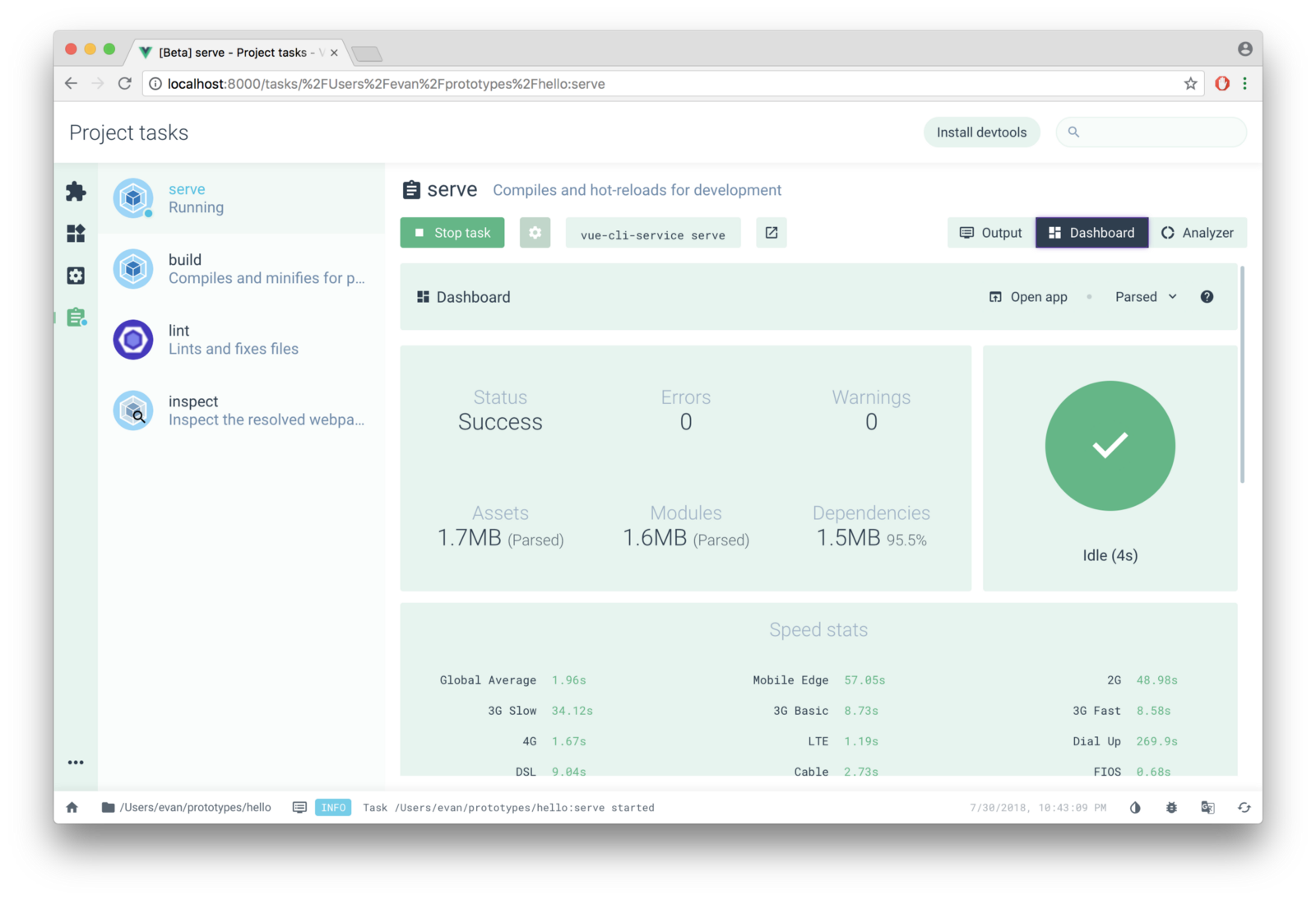
从一张图开始源码的分析
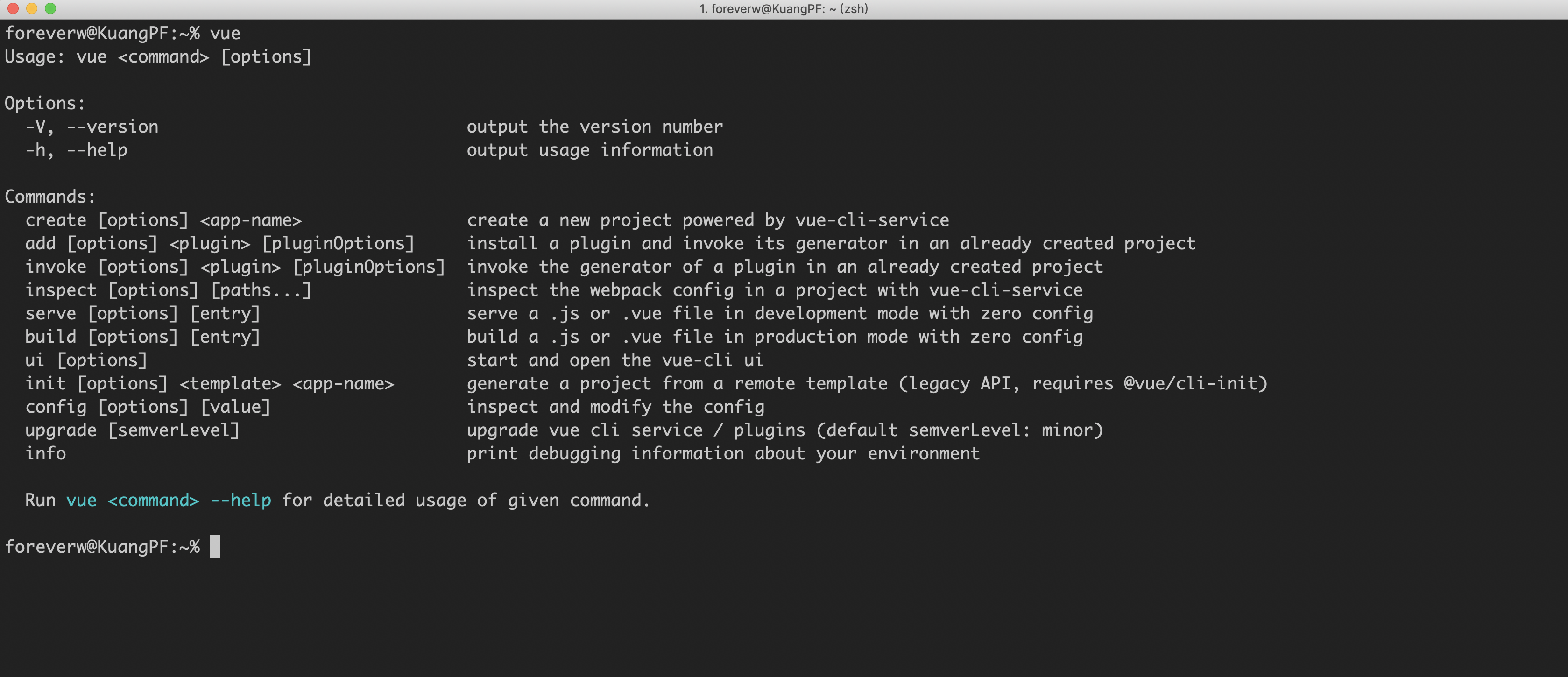
安装 vue-cli
npm install -g @vue/cli
# OR
yarn global add @vue/cli
2
3
在安装 vue-cli 之后,执行 vue 命令,就可以得到上面图片中的内容,从这个图片中可以看出,vue-cli 一共有 11 种命令:
- create
- add
- invoke
- inspect
- serve
- build
- ui
- init
- config
- upgrade
- info
我们就逐个开始分析。
# 常见 npm 包
在进去 vue-cli 源码学习之前,这里先介绍下在 vue-cli 项目中用到的一些必备的 npm 包,这样在后面分析源码的时候会比较快的理解(handlebars,metalsmith,consolidate 主要用于 vue init 命令)。
- commander (opens new window):node.js command-line interfaces made easy。
- Inquirer (opens new window):A collection of common interactive command line user interfaces。
- execa (opens new window):A better child_process (opens new window)。
- handlebars (opens new window):一个 javascript 语以模版库。
- metalsmith (opens new window);An extremely simple, pluggable static site generator。
- chalk (opens new window):Terminal string styling done right。
- download-git-repo (opens new window):Download and extract a git repository (GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket) from node。
- consolidate (opens new window):Template engine consolidation library for node.js 。
下面逐个介绍:
# commander
commander 是一款重量轻,表现力和强大的命令行框架,提供了用户命令行输入和参数解析强大功能。
#!/usr/bin/env node
const program = require('commander')
program
.version('0.0.1')
.command('rmdir <dir> [otherDirs...]')
.action(function(dir, otherDirs) {
console.log('rmdir %s', dir);
if (otherDirs) {
otherDirs.forEach(function(oDir) {
console.log('rmdir %s', oDir);
});
}
});
program.parse(process.argv);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
这段代码为 commander.js 官方的一个示例,它展示了 commander.js 可变参数的特性,可以在 action 的回调中获取对应的参数,当然也可以通过 process.argv 获取,commander.js 中文文档 (opens new window)。
# Inquirer
Inquirer 为交互式命令行工具,比如执行 vue create 命令会有以下的命令行交互:
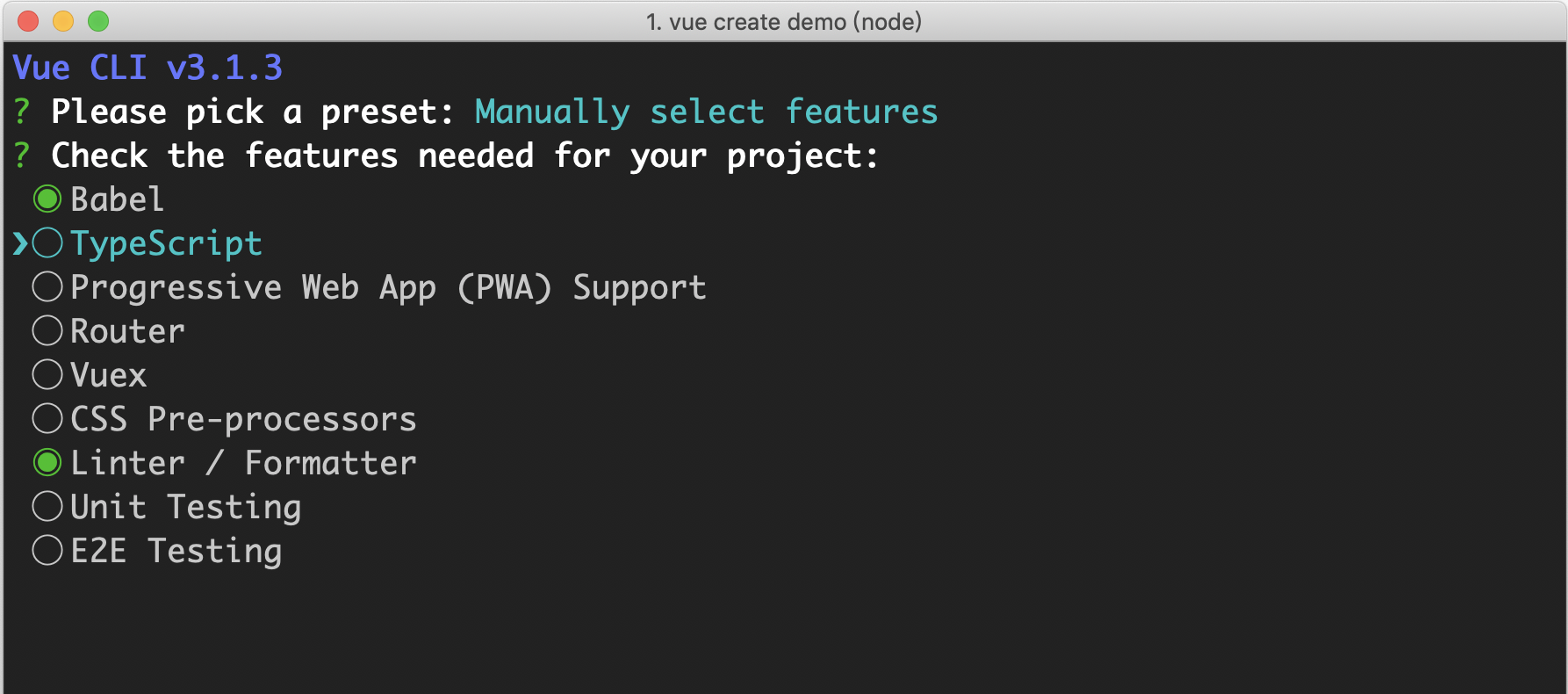
Inquirer 的基本使用如下:
var inquirer = require('inquirer');
inquirer
.prompt([
/* Pass your questions in here */
])
.then(answers => {
// Use user feedback for... whatever!!
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
inquirer.prompt 接受一个 questions 数组, 一个 question 对象包含 type,name, message, default 等等字段,然后通过回调获取命令行交互的值,详细文档 (opens new window)。
# execa
execa 是可以调用 shell 和本地外部程序的 javascript 封装。会启动子进程执行,支持多操作系统,包括 windows,如果父进程退出,则生成的全部子进程都被杀死。它是在 Node.js 内置的 child_process.exec 基础上进行了提升,比如更好地支持 windows 平台,以及提供 Promise 的接口等等。可以看一个很简单的例子:
const execa = require('execa');
(async () => {
const {stdout} = await execa('echo', ['unicorns']);
console.log(stdout);
//=> 'unicorns'
})();
2
3
4
5
6
7
上面例子就是执行 echo unicorns 命令输出 unicorns。关于 execa 更多的用法可查看 详细文档 (opens new window)。
# handlebars
handlebars 是一个 javascript 语义模版库,而且与 Mustache 模板 是兼容的,通过一个 demo 来感受下:
var source = "<p>Hello, my name is {{name}}. I am from {{hometown}}. I have " +
"{{kids.length}} kids:</p>" +
"<ul>{{#kids}}<li>{{name}} is {{age}}</li>{{/kids}}</ul>";
var template = Handlebars.compile(source);
var data = { "name": "Alan", "hometown": "Somewhere, TX",
"kids": [{"name": "Jimmy", "age": "12"}, {"name": "Sally", "age": "4"}]};
var result = template(data);
// Would render:
// <p>Hello, my name is Alan. I am from Somewhere, TX. I have 2 kids:</p>
// <ul>
// <li>Jimmy is 12</li>
// <li>Sally is 4</li>
// </ul>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
这是官方的一个 demo, 就是通过 Handlebars 的 compile 方法将模板编译成 html 。在 vue-cli 的 init 命令中,利用 Handlebars.registerHelper 方法注册了一些 helper,这样就可以在模板中方便的使用这些 helper,详细文档 (opens new window)。
# metalsmith
metalsmith 一个静态网站生成器,可以用在批量处理模板的场景,和 hexo 类似。它最大的特点就是所有的逻辑都是由插件处理,你只需要将这些插件用 metalsmith 连接起来使用即可,比如官方的一个 demo:
Metalsmith(__dirname)
.use(markdown())
.use(layouts('handlebars'))
.build(function(err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('Build finished!');
});
2
3
4
5
6
7
这段代码就是通过使用 metalsmith-markdown (opens new window) 和 metalsmith-layouts (opens new window) 插件 将 markdown 文件以 handlebars 的模板形式来生成html 文件,在 vue-cli 的 init 命令中使用了三个插件:askQuestions filterFiles renderTemplateFiles 从这名字就知道这个插件的作用了。编写 metalsmith 其实不是很难,官方对插件的编写介绍地比较详细,示例代码:
metalsmith-myplugin:
// we would like you to use debug
var debug = require('debug')('metalsmith-myplugin');
var multimatch = require('multimatch');
// Expose `plugin`.
module.exports = plugin;
function plugin(opts){
opts.pattern = opts.pattern || [];
return function (files, metalsmith, done){
setImmediate(done);
Object.keys(files).forEach(function(file){
if(multimatch(file, opts.pattern).length) {
debug('myplugin working on: %s', file);
//
// here would be your code
//
}
});
};
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
关于 metalsmith 的更多介绍以及语法可查看详细文档 (opens new window)。
# chalk
chalk 是用于修改控制台字符串的样式,包括字体样式(加粗),颜色以及背景颜色等。

使用比较简单:
const chalk = require('chalk');
console.log(chalk.blue('Hello world!'));
2
更多的用法以及 API 可查看详细文档 (opens new window)。
# download-git-repo
download-git-repo 是用于 从 GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket 下载一个 git 仓库,API 如下:
download(repository, destination, options, callback)
- repository:仓库地址。
- destination:存放下载 git 仓库的路径。
- options:选项,clone。是以 http download 的形式还是 git clone 的形式下载。其中 git clone 的形式支持下载 private 仓库。
- callback:下载完成地回调。
更多例子可查看 详细文档 (opens new window)。
# consolidate
consolidate 是一个模版引擎整合库,它的作用是把一些著名的模板引擎适配成 Express 兼容的接口。在 vue-cli 的 init 命令中利用 consolidate.handlebars.render 是实现模版的渲染。在 /example/metalsmith 目录里有个 demo,就是通过 metalsmith 以及consolidate.handlebars.render 方法将一个 package.json 以 handlebars 的模板引擎来渲染,在项目里运行
npm run metalsmith
希望可以通过这个小 demo 可以比较好地理解 metalsmith, handlebars ,consolidate 以及inquirer,关于 consolidate 的更多语法请查看详细文档 (opens new window)。
# 总结
这部分主要介绍了在利用 node 搭建脚手架工具时一些常见的 npm 包,对这些 npm 包进行一定的了解后,在后面看源码的时候会比较容易些,下面开始进行源码分析。
# vue create
# create 入口
源码目录: packages/@vue/cli/lib/create.js 。
作用: create a new project powered by vue-cli-service 。
vue create 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js 中:
program
.command('create <app-name>')
.description('create a new project powered by vue-cli-service')
.option('-p, --preset <presetName>', 'Skip prompts and use saved or remote preset')
.option('-d, --default', 'Skip prompts and use default preset')
.option('-i, --inlinePreset <json>', 'Skip prompts and use inline JSON string as preset')
.option('-m, --packageManager <command>', 'Use specified npm client when installing dependencies')
.option('-r, --registry <url>', 'Use specified npm registry when installing dependencies (only for npm)')
.option('-g, --git [message]', 'Force git initialization with initial commit message')
.option('-n, --no-git', 'Skip git initialization')
.option('-f, --force', 'Overwrite target directory if it exists')
.option('-c, --clone', 'Use git clone when fetching remote preset')
.option('-x, --proxy', 'Use specified proxy when creating project')
.option('-b, --bare', 'Scaffold project without beginner instructions')
.action((name, cmd) => {
const options = cleanArgs(cmd)
// --git makes commander to default git to true
if (process.argv.includes('-g') || process.argv.includes('--git')) {
options.forceGit = true
}
require('../lib/create')(name, options)
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
一看这么多参数,不要方,一个一个地来解释这些参数:
-p, --preset <presetName> 忽略提示符并使用已保存的或远程的预设选项
-d, --default 忽略提示符并使用默认预设选项
-i, --inlinePreset <json> 忽略提示符并使用内联的 JSON 字符串预设选项
-m, --packageManager <command> 在安装依赖时使用指定的 npm 客户端
-r, --registry <url> 在安装依赖时使用指定的 npm registry
-g, --git [message] 强制 / 跳过 git 初始化,并可选的指定初始化提交信息
-n, --no-git 跳过 git 初始化
-f, --force 覆写目标目录可能存在的配置
-c, --clone 使用 git clone 获取远程预设选项
-x, --proxy 使用指定的代理创建项目
-b, --bare 创建项目时省略默认组件中的新手指导信息
-h, --help 输出使用帮助信息
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
以上这些解释只是从 vue-cli 官网搬运过来了的,在下一节将整体介绍 vue create 命令主要由哪几部分构成的。
# 整体分析
先通过一张流程图大致聊了解下 vue create 的过程:
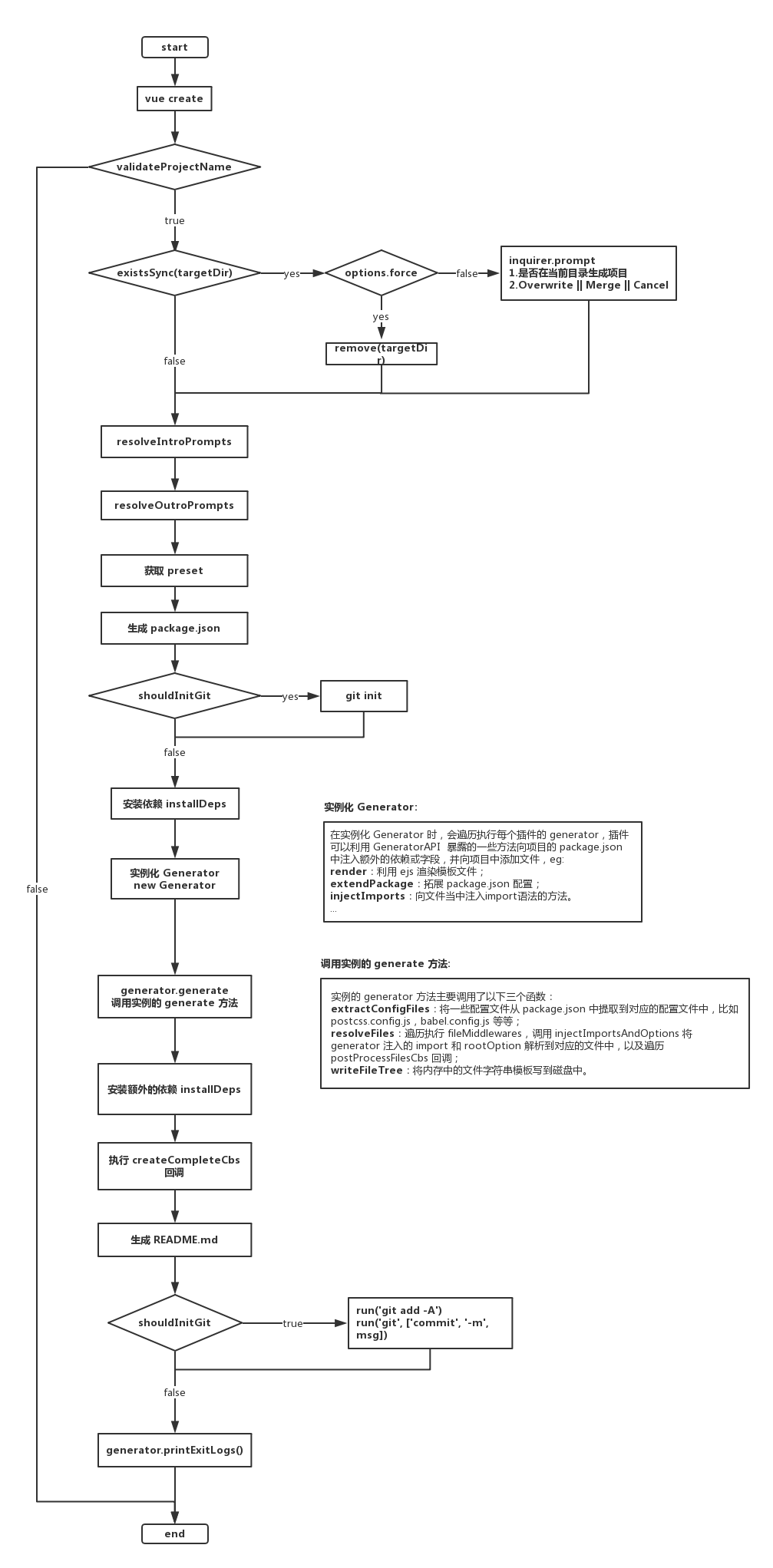
从这个图可以直观地感受到 vue create 整个过程还是比较复杂的,为了比较清楚的讲解整个过程,大致分为了 5 个部分,如下:
下面将一节一节的来分析 vue create 的源码。
# 基础验证
当执行 vue create 命令的时候会加载 cli/lib/create.js 中的 create 函数。在 create 函数里会先定义以下几个变量:
const cwd = options.cwd || process.cwd() // 当前目录
const inCurrent = projectName === '.' // 是否在当前目录
const name = inCurrent ? path.relative('../', cwd) : projectName // 项目名称
const targetDir = path.resolve(cwd, projectName || '.') // 生成项目的目录
2
3
4
比较重要的就是 name 和 targetDir 这两个,在下面函数运行过程中会使用到。接下来执行函数 validateProjectName 利用 npm 包 validate-npm-package-name (opens new window) 判断项目名称是否符合 npm 包名规范,并输出相应的 errors 或者 warnings。
在验证包名之后,会判断项目目录是否与当前已有目录重复。
if (fs.existsSync(targetDir)) {
if (options.force) {
await fs.remove(targetDir)
} else {
await clearConsole()
if (inCurrent) {
const { ok } = await inquirer.prompt([
{
name: 'ok',
type: 'confirm',
message: `Generate project in current directory?`
}
])
if (!ok) {
return
}
} else {
const { action } = await inquirer.prompt([
{
name: 'action',
type: 'list',
message: `Target directory ${chalk.cyan(targetDir)} already exists. Pick an action:`,
choices: [
{ name: 'Overwrite', value: 'overwrite' },
{ name: 'Merge', value: 'merge' },
{ name: 'Cancel', value: false }
]
}
])
if (!action) {
return
} else if (action === 'overwrite') {
console.log(`\nRemoving ${chalk.cyan(targetDir)}...`)
await fs.remove(targetDir)
}
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
这段代码比较容易读懂,主要就是当存在相同项目目录的时候调用 inquirer.prompt 来询问是否要 Overwrite || Merge || Cancel。
TIP
当带有 -f || --force 的时候会跳过这些交互,即 options.force = true。
基础验证这快大致就这些,下一个开始分析获取预设选项(preset)。
# 获取预设选项(preset)
在开始分析之前简单描述下什么是 vue-cli-preset, 一个 Vue CLI preset 是一个包含创建新项目所需预定义选项和插件的 JSON 对象,让用户无需在命令提示中选择它们:
{
"useConfigFiles": true,
"router": true,
"vuex": true,
"cssPreprocessor": "sass",
"plugins": {
"@vue/cli-plugin-babel": {},
"@vue/cli-plugin-eslint": {
"config": "airbnb",
"lintOn": ["save", "commit"]
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
更多关于 preset 可以前往 vue-cli 官网 插件和 Preset# (opens new window)。
在基础验证完成以后会创建一个 Creator 实例:
const creator = new Creator(name, targetDir, getPromptModules())
# getPromptModules
在分析 Creator 之前先看下 getPromptModules() 获取到的是什么。getPromptModules() 获取了 babel,typescript,pwa,router,vuex, cssPreprocessors,linter,unit,e2e 的 Prompt 的配置信息,以 unit 为例:
module.exports = cli => {
cli.injectFeature({
name: 'Unit Testing',
value: 'unit',
short: 'Unit',
description: 'Add a Unit Testing solution like Jest or Mocha',
link: 'https://cli.vuejs.org/config/#unit-testing',
plugins: ['unit-jest', 'unit-mocha']
})
cli.injectPrompt({
name: 'unit',
when: answers => answers.features.includes('unit'),
type: 'list',
message: 'Pick a unit testing solution:',
choices: [
{
name: 'Mocha + Chai',
value: 'mocha',
short: 'Mocha'
},
{
name: 'Jest',
value: 'jest',
short: 'Jest'
}
]
})
cli.onPromptComplete((answers, options) => {
if (answers.unit === 'mocha') {
options.plugins['@vue/cli-plugin-unit-mocha'] = {}
} else if (answers.unit === 'jest') {
options.plugins['@vue/cli-plugin-unit-jest'] = {}
}
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
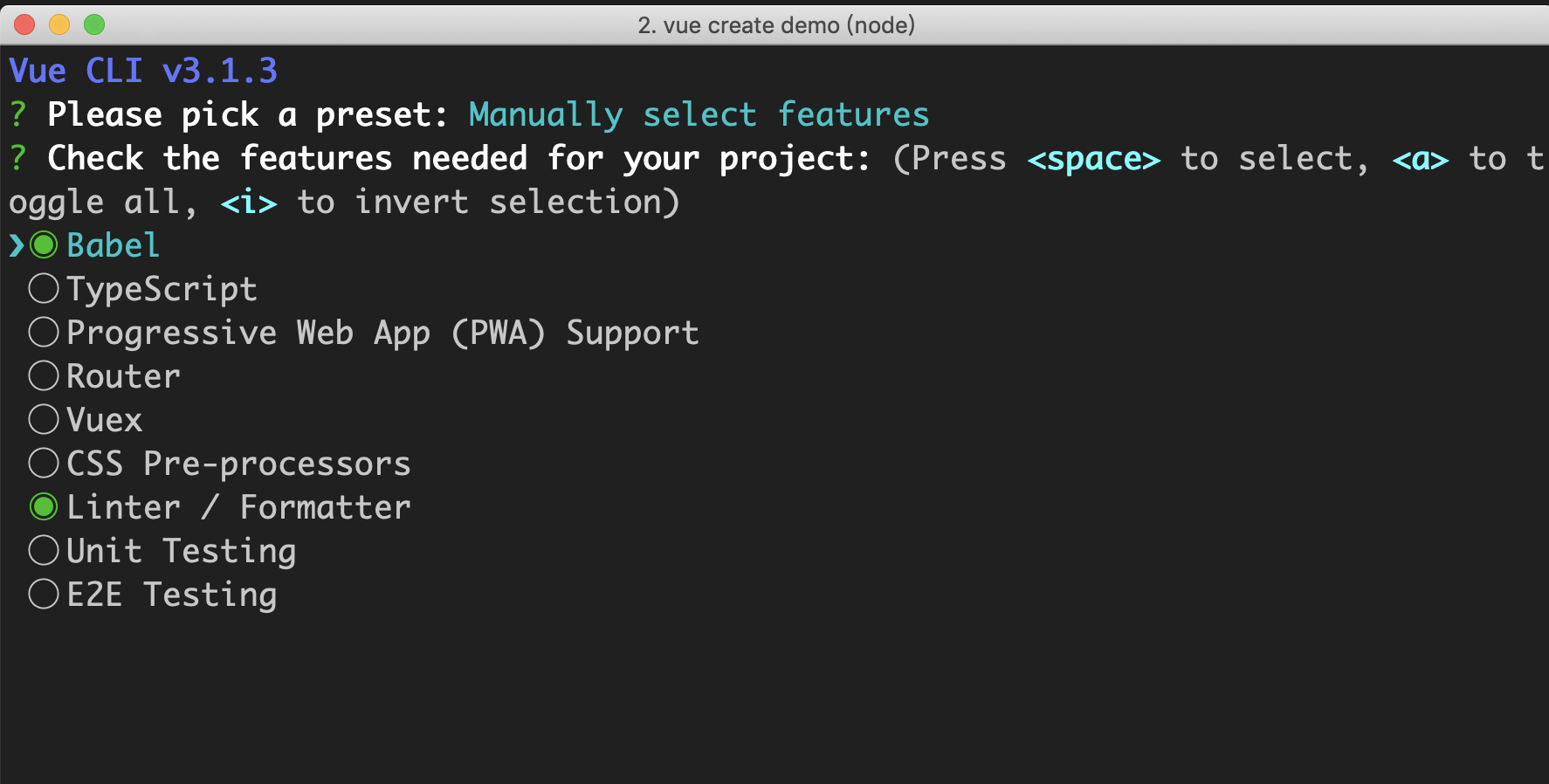
cli.injectFeature
cli.injectFeature 是注入 featurePrompt,即初始化项目时选择 babel,typescript,pwa 等等,如下图:
cli.injectPrompt
cli.injectPrompt 是根据选择的 featurePrompt 然后注入对应的 prompt,当选择了 unit,接下来会有以下的 prompt,选择 Mocha + Chai 还是 Jest:
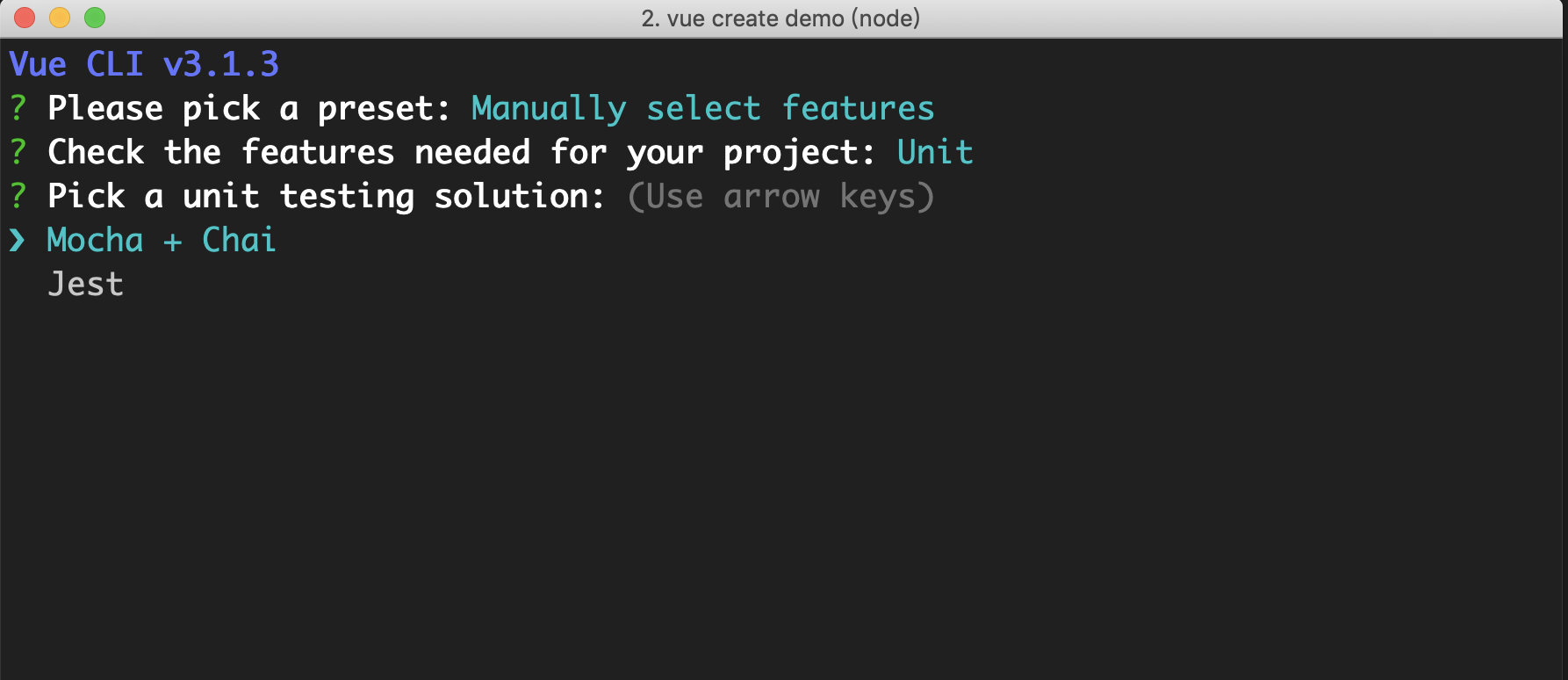
cli.onPromptComplete
cli.onPromptComplete 就是一个回调,会根据选择来添加对应的插件, 当选择了 mocha ,那么就会添加 @vue/cli-plugin-unit-mocha 插件。
# new Creator()
搞清楚了 getPromptModules 之后,下面开始看一下初始化 Creator 实例发生了什么,直接看代码:
constructor (name, context, promptModules) {
super()
this.name = name
this.context = process.env.VUE_CLI_CONTEXT = context
const { presetPrompt, featurePrompt } = this.resolveIntroPrompts() // 获取了 presetPrompt list,在初始化项目的时候提供选择
this.presetPrompt = presetPrompt // presetPrompt list
this.featurePrompt = featurePrompt // babal, pwa, e2e etc.
this.outroPrompts = this.resolveOutroPrompts() // 存放项目配置的文件(package.json || congfig.js) 以及是否将 presetPrompts 存放起来
this.injectedPrompts = [] // 对应 feature 的 Prompts
this.promptCompleteCbs = [] // injectedPrompts 的回调
this.createCompleteCbs = []
this.run = this.run.bind(this)
const promptAPI = new PromptModuleAPI(this)
/**
* 1. 将 babel, e2e, pwa 等 push 到 featurePrompt.choices 中,在选择项目需要配置哪些时显示出来 (checkbox);
* 2. 将 babel, e2e, pwa 等 push 到 injectedPrompts 中,当设置了 feature 会对应通过 Prompts 来进一步选择哪种模式,比如当选择了 E2E Testing ,然后会再次让你
* 选择哪种 E2E Testing,即, Cypress (Chrome only) || Nightwatch (Selenium-based);
* 3. 将每中 feature 的 onPromptComplete push 到 promptCompleteCbs,在后面会根据选择的配置来安装对应的 plugin。
*/
promptModules.forEach(m => m(promptAPI))
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
这段代码主要看下 PromptModuleAPI,源码如下:
module.exports = class PromptModuleAPI {
constructor (creator) {
this.creator = creator
}
injectFeature (feature) {
this.creator.featurePrompt.choices.push(feature)
}
injectPrompt (prompt) {
this.creator.injectedPrompts.push(prompt)
}
injectOptionForPrompt (name, option) {
this.creator.injectedPrompts.find(f => {
return f.name === name
}).choices.push(option)
}
onPromptComplete (cb) {
this.creator.promptCompleteCbs.push(cb)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
PromptModuleAPI 实例会调用它的实例方法,然后将 injectFeature, injectPrompt, injectOptionForPrompt, onPromptComplete保存到 Creator实例对应的变量中。
最后遍历 getPromptModules 获取的 promptModules,传入实例 promptAPI,初始化 Creator 实例中 featurePrompt, injectedPrompts, promptCompleteCbs 变量。
# getPreset
在创建一个 Creator 实例后,然后调用了 create 方法
await creator.create(options)
create 开始是获取 preset ,源码如下:
const isTestOrDebug = process.env.VUE_CLI_TEST || process.env.VUE_CLI_DEBUG
console.log('before creating......')
// name: demo
// context: targetDir
const { run, name, context, createCompleteCbs } = this
if (!preset) {
if (cliOptions.preset) {
// vue create foo --preset bar
preset = await this.resolvePreset(cliOptions.preset, cliOptions.clone)
} else if (cliOptions.default) {
// vue create foo --default
preset = defaults.presets.default // 使用默认预设选项
} else if (cliOptions.inlinePreset) { // 使用内联的 JSON 字符串预设选项
// vue create foo --inlinePreset {...}
try {
preset = JSON.parse(cliOptions.inlinePreset)
} catch (e) {
error(`CLI inline preset is not valid JSON: ${cliOptions.inlinePreset}`)
exit(1)
}
} else {
// eg: vue create demo
preset = await this.promptAndResolvePreset()
}
}
// clone before mutating
preset = cloneDeep(preset)
// inject core service
preset.plugins['@vue/cli-service'] = Object.assign({ // 注入核心 @vue/cli-service
projectName: name
}, preset, {
bare: cliOptions.bare
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
先判断 vue create 命令是否带有 -p 选项,如果有的话会调用 resolvePreset 去解析 preset。resolvePreset 函数会先获取 ~/.vuerc 中保存的 preset, 然后进行遍历,如果里面包含了 -p 中的 <presetName>,则返回~/.vuerc 中的 preset。如果没有则判断是否是采用内联的 JSON 字符串预设选项,如果是就会解析 .json 文件,并返回 preset,还有一种情况就是从远程获取 preset(利用 download-git-repo 下载远程的 preset.json)并返回。
上面的情况是当 vue create 命令带有 -p 选项的时候才会执行,如果没有就会调用 promptAndResolvePreset 函数利用 inquirer.prompt 以命令后交互的形式来获取 preset,下面看下 promptAndResolvePreset 函数的源码:
async promptAndResolvePreset (answers = null) {
// prompt
if (!answers) {
await clearConsole(true)
answers = await inquirer.prompt(this.resolveFinalPrompts())
}
debug('vue-cli:answers')(answers)
if (answers.packageManager) {
saveOptions({
packageManager: answers.packageManager
})
}
let preset
if (answers.preset && answers.preset !== '__manual__') { // 如果是选择使用本地保存的 preset (~/.vuerc)
preset = await this.resolvePreset(answers.preset)
} else {
// manual
preset = {
useConfigFiles: answers.useConfigFiles === 'files',
plugins: {}
}
answers.features = answers.features || []
// run cb registered by prompt modules to finalize the preset
this.promptCompleteCbs.forEach(cb => cb(answers, preset))
}
// validate
validatePreset(preset)
// save preset
if (answers.save && answers.saveName) {
savePreset(answers.saveName, preset)
}
debug('vue-cli:preset')(preset)
return preset
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
在调用 inquirer.prompt 之前利用 this.resolveFinalPrompts() 获取了最后的 prompts,到这里有些同学可能就有点晕了,到底有多少个 prompt,别急,下面将 简单介绍下,查看 this.resolveFinalPrompts() 源码:
resolveFinalPrompts () {
// patch generator-injected prompts to only show in manual mode
// 将所有的 Prompt 合并,包含 preset,feature,injected,outro,只有当选择了手动模式的时候才会显示 injectedPrompts
this.injectedPrompts.forEach(prompt => {
const originalWhen = prompt.when || (() => true)
prompt.when = answers => {
return isManualMode(answers) && originalWhen(answers)
}
})
const prompts = [
this.presetPrompt,
this.featurePrompt,
...this.injectedPrompts,
...this.outroPrompts
]
debug('vue-cli:prompts')(prompts)
return prompts
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
比较容易的就可以看出作用就是将 presetPrompt, featurePrompt, injectedPrompts, outroPrompts 合并成一个数组进行返回,这几个 Prompt 的含义如下:
presetPrompt: 预设选项 prompt,当上次以 Manually 模式进行了预设选项,并且保存到了 ~/.vuerc 中,那么在初始化项目时就会列出已经保存的 preset,并提供选择。
featurePrompt:项目的一些 feature,就是选择 babel,typescript,pwa,router,vuex,cssPreprocessors,linter,unit,e2e。
injectedPrompts:当选择了 feature 后,就会为对应的 feature 注入 prompts,比如你选择了 unit,那么就会让你选择模式:
Mocha + Chai还是JestoutroPrompts
: 其他的 prompt,包含:
- 将 Babel, PostCSS, ESLint 等等的配置文件存放在 package.json 中还是存放在 config 文件中;
- 是否需要将这次设置的 preset 保存到本地,如果需要则会进一步让你输入名称进行保存;
- 安装依赖是选择 npm 还是 yarn。
inquirer.prompt 执行完成后会返回 answers,如果选择了本地保存的 preset 或者 default,则调用 resolvePreset 进行解析 preset,否则遍历 promptCompleteCbs 执行 injectFeature 和 injectPrompt 的回调,将对应的插件赋值到 options.plugins 中,以 unit 为例:
cli.onPromptComplete((answers, options) => {
if (answers.unit === 'mocha') {
options.plugins['@vue/cli-plugin-unit-mocha'] = {}
} else if (answers.unit === 'jest') {
options.plugins['@vue/cli-plugin-unit-jest'] = {}
}
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
如果 feature 选择了 unit,并且 unit 模式选择的是 Mocha + Chai,则添加 @vue/cli-plugin-unit-mocha 插件,如果选择的是 Jest 则添加 @vue/cli-plugin-unit-jest 插件。
在获取到 preset 之后,还会向 preset 的插件里面注入核心插件 @vue/cli-service, 它是调用 vue-cli-service <command> [...args] 时创建的类。 负责管理内部的 webpack 配置、暴露服务和构建项目的命令等。
到这里获取预设选项(preset)大致分析完了,在下节将会分析依赖的安装。
# 依赖安装(installDeps)
在上节中我们分析了获取 preset ,通过 preset 我们可以知道每个 feature 的配置以及整个项目所需的一些插件,接下来我们继续看源码。
const packageManager = (
cliOptions.packageManager ||
loadOptions().packageManager ||
(hasYarn() ? 'yarn' : 'npm')
)
await clearConsole() // 清空控制台
logWithSpinner(`✨`, `Creating project in ${chalk.yellow(context)}.`)
this.emit('creation', { event: 'creating' })
// get latest CLI version
const { latest } = await getVersions()
// generate package.json with plugin dependencies
const pkg = {
name,
version: '0.1.0',
private: true,
devDependencies: {}
}
const deps = Object.keys(preset.plugins)
deps.forEach(dep => {
if (preset.plugins[dep]._isPreset) {
return
}
pkg.devDependencies[dep] = (
preset.plugins[dep].version ||
((/^@vue/.test(dep) && latest[dep]) ? `^${latest[dep]}` : `latest`)
)
})
// write package.json
await writeFileTree(context, {
'package.json': JSON.stringify(pkg, null, 2)
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
这段代码主要有两个作用:获取最新 CLI (包含插件)的版本 和 生成 package.json,接下来一个一个地看。
# getVersions
getVersions 的代码不多,看下比较核心的代码:
module.exports = async function getVersions () {
if (sessionCached) {
return sessionCached
}
let latest
const local = require('vue-cli-version-marker').devDependencies
if (process.env.VUE_CLI_TEST || process.env.VUE_CLI_DEBUG) {
return (sessionCached = {
current: local,
latest: local
})
}
if (!fs.existsSync(fsCachePath)) {
// if the cache file doesn't exist, this is likely a fresh install
// then create a cache file with the bundled version map
await fs.writeFile(fsCachePath, JSON.stringify(local))
}
const cached = JSON.parse(await fs.readFile(fsCachePath, 'utf-8'))
const lastChecked = (await fs.stat(fsCachePath)).mtimeMs
const daysPassed = (Date.now() - lastChecked) / (60 * 60 * 1000 * 24)
if (daysPassed > 1) { // 距离上次检查更新超过一天
// if we haven't check for a new version in a day, wait for the check
// before proceeding
latest = await getAndCacheLatestVersions(cached)
} else {
// Otherwise, do a check in the background. If the result was updated,
// it will be used for the next 24 hours.
getAndCacheLatestVersions(cached) // 后台更新
latest = cached
}
return (sessionCached = {
current: local,
latest
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
这段代码按顺序读下应该就知道其中的作用了,简单说下就注意两个变量:
- local:本地 CLI 以及插件的版本
- latest:远程 CLI 以及插件的版本
local 和 latest 包含了 CLI 以及相关插件的版本,它们可以用于判断 @vue/cli 是否需要更新以及初始化项目中相关插件的版本。还有点需要注意的是,获取 CLI 的版本并不是直接获取, 而是通过 vue-cli-version-marker (opens new window) npm 包获取的 CLI 版本,为什么会这样做,主要原因有两点:
- vue-cli 从 3.0(@vue/cli) 开始就放在了 @vue 下面,即是一个 scoped package, 而 scoped package 又不支持通过
npm registry来获取 latest 版本信息。比如 vue-cli-version-marker/latest (opens new window)可以正常访问,而 @vue/cli/latest (opens new window) 则不可以。
- vue-cli 从 3.0(@vue/cli) 开始就放在了 @vue 下面,即是一个 scoped package, 而 scoped package 又不支持通过
- 获取 scoped packages 的数据比获取 unscoped package 通常要慢 300ms。
正是由于上述两个原因,因此通过 unscoped package vue-cli-version-marker 来获取 CLI 版本,vue-cli-version-marker 的内容比较简单,就是一个 package.json,通过获取里面 devDependencies 的版本信息,从而获取 @vue/cli 以及一些插件的版本号。获取了插件版本之后遍历 preset 中所有 plugin 为其初始化版本号,并调用 writeFileTree 生成 package.json 。
# installDeps
在生成 package.json 之后,我们再继续看下面的代码:
// intilaize git repository before installing deps
// so that vue-cli-service can setup git hooks.
const shouldInitGit = await this.shouldInitGit(cliOptions)
if (shouldInitGit) {
logWithSpinner(`🗃`, `Initializing git repository...`)
this.emit('creation', { event: 'git-init' })
await run('git init')
}
// install plugins
stopSpinner()
log(`⚙ Installing CLI plugins. This might take a while...`)
log()
this.emit('creation', { event: 'plugins-install' })
if (isTestOrDebug) {
// in development, avoid installation process
await require('./util/setupDevProject')(context) // @vue/cli-service/bin/vue-cli-service
} else {
await installDeps(context, packageManager, cliOptions.registry)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
这段代码会先调用 shouldInitGit 来判断是否需要 git 初始化,判断的情形有以下几种:
- 没有安装 git (
!hasGit()):false; - vue create 含有 --git 或者 -g 选项:true;
- vue create 含有 --no-git 或者 -n 选项:false;
- 生成项目的目录是否已经含有 git (
!hasProjectGit(this.context)):如果有,则返回 false,否则返回 true。
在判断完是否需要 git 初始化项目后,接下来就会调用 installDeps 安装依赖,还是看下 installDeps 的源码:
exports.installDeps = async function installDeps (targetDir, command, cliRegistry) {
const args = []
if (command === 'npm') {
args.push('install', '--loglevel', 'error')
} else if (command === 'yarn') {
// do nothing
} else {
throw new Error(`Unknown package manager: ${command}`)
}
await addRegistryToArgs(command, args, cliRegistry)
debug(`command: `, command) // DEBUG=vue-cli:install vue create demo
debug(`args: `, args)
await executeCommand(command, args, targetDir)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
源码很简洁,里面又先调用了 addRegistryToArgs 函数,它的作用就是安装依赖是指定安装源,如果 vue create 还有 -r 选项则采用设置的安装源,否则调用 shouldUseTaobao 函数来判断是否需要使用淘宝 NPM 镜像源。实现原理就是发送两个 Promise 使用默认安装源和淘宝镜像源去请求同一个 npm 包,然后利用 Promise.race 看在哪种源下返回结果更快就将此 设置为安装源,另外如果 ~/.vuerc 中设置了useTaobaoRegistry,则使用设置的安装源。设置了安装源之后则调用 executeCommand 函数利用 execa 执行 npm 或者 yarn 安装命令。
到这里安装依赖就大致介绍完了,在下面一节将介绍 vue create 核心部分 Generator。
# Generator
在安装完依赖以后,就会调用 resolvePlugins,作用就是加载每个插件的 generator ,并且如果插件需要进行命令行交互的话会执行 inquirer.prompt 获取 option。 在此之后会实例化一个 Generator ,看代码:
const generator = new Generator(context, {
pkg,
plugins,
completeCbs: createCompleteCbs
})
2
3
4
5
在实例化一个 Generator 的时候会初始化一些成员变量,最重要的就是调用插件的 generators,不同于 1.x/2.x 基于模板的脚手架,Vue-cli3.0 采用了一套 基于插件的架构,到这里就会交给各个插件去执行了,看一下 Generator 实例化的代码:
module.exports = class Generator {
constructor (context, {
pkg = {},
plugins = [],
completeCbs = [],
files = {},
invoking = false
} = {}) {
this.context = context
this.plugins = plugins
this.originalPkg = pkg
this.pkg = Object.assign({}, pkg)
this.imports = {}
this.rootOptions = {}
this.completeCbs = completeCbs
this.configTransforms = {} // 插件通过 GeneratorAPI 暴露的 addConfigTransform 方法添加如何提取配置文件
this.defaultConfigTransforms = defaultConfigTransforms // 默认的配置文件
this.reservedConfigTransforms = reservedConfigTransforms // 保留的配置文件 vue.config.js
this.invoking = invoking
// for conflict resolution
this.depSources = {}
// virtual file tree
this.files = files
this.fileMiddlewares = [] // receives the virtual files tree object, and an ejs render function
this.postProcessFilesCbs = []
// exit messages
this.exitLogs = []
const cliService = plugins.find(p => p.id === '@vue/cli-service')
const rootOptions = cliService
? cliService.options
: inferRootOptions(pkg)
// apply generators from plugins
// 调用插件的 generators
plugins.forEach(({ id, apply, options }) => {
// 每个插件对应生成一个 GeneratorAPI 实例,并将实例 api 传入插件暴露出来的 generator 函数
const api = new GeneratorAPI(id, this, options, rootOptions)
apply(api, options, rootOptions, invoking)
})
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
接下来看一下 GeneratorAPI。
# GeneratorAPI
GeneratorAPI 是一个比较重要的部分了,前面说过 vue-cli 3.0 是基于一套插件架构的,那么如果插件需要自定义项目模板、修改模板中的一些文件或者添加一些依赖 的话怎么处理呢。方法是 @vue/cli 插件所提供的 generator 向外暴露一个函数,接收的第一个参数 api,然后通过该 api 提供的方法去完成应用的拓展工作,这里所说 的 api 就是 GeneratorAPI,下面看一下 GeneratorAPI 提供了哪些方法。
- hasPlugin:判断项目中是否有某个插件
- extendPackage:拓展 package.json 配置
- render:利用 ejs 渲染模板文件
- onCreateComplete:内存中保存的文件字符串全部被写入文件后的回调函数
- exitLog:当 generator 退出的时候输出的信息
- genJSConfig:将 json 文件生成为 js 配置文件
- injectImports:向文件当中注入import语法的方法
- injectRootOptions:向 Vue 根实例中添加选项
- ...
下面就以 @vue/cli-service 为例,来简单熟悉下 GeneratorAPI。首先看一下 @vue/cli-service/generator/index.js
module.exports = (api, options) => {
/* 渲染 ejs 模板 */
api.render('./template', {
doesCompile: api.hasPlugin('babel') || api.hasPlugin('typescript')
})
// 扩展 package.json
api.extendPackage({
scripts: {
'serve': 'vue-cli-service serve',
'build': 'vue-cli-service build'
},
dependencies: {
'vue': '^2.5.17'
},
devDependencies: {
'vue-template-compiler': '^2.5.17'
},
'postcss': {
'plugins': {
'autoprefixer': {}
}
},
browserslist: [
'> 1%',
'last 2 versions',
'not ie <= 8'
]
})
// 如果 preset 中包含 vue-router
if (options.router) {
require('./router')(api, options)
}
// 如果 preset 中包含 vuex
if (options.vuex) {
require('./vuex')(api, options)
}
// 如果 preset 中包含 cssPreprocessor,即选择了 css 预处理器
if (options.cssPreprocessor) {
const deps = {
sass: {
'node-sass': '^4.9.0',
'sass-loader': '^7.0.1'
},
less: {
'less': '^3.0.4',
'less-loader': '^4.1.0'
},
stylus: {
'stylus': '^0.54.5',
'stylus-loader': '^3.0.2'
}
}
api.extendPackage({
devDependencies: deps[options.cssPreprocessor]
})
}
// additional tooling configurations
if (options.configs) {
api.extendPackage(options.configs)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
看一下 @vue/cli-service generator 代码,然后结合 GeneratorAPI 所暴露的方法,自己再感悟下,大概就可以明白插件利用 GeneratorAPI 暴露的方法 做了一些什么事情,也可以初步感受到 vue-cli 3.0 的插件机制,将所有功能都交给插件去完成。对于 vue-cli 3.0 内置的插件,比如:@vue/cli-plugin-eslint 、@vue/cli-plugin-pwa 等等,以及其他第三方插件,他们的 generator 作用都是一样都可以向项目的 package.json 中注入额外的依赖或字段,并向项目中添加文件。
在实例化 Generator 之后,就会调用实例的 generate 放在,此时就差不多进入到了生成项目文件的阶段了。大致可以分为三部分,extractConfigFiles(提取配置文件), resolveFiles(模板渲染)和 writeFileTree(在磁盘上生成文件)。
# extractConfigFiles
提取配置文件指的是将一些插件(比如 eslint,babel)的配置从 package.json 的字段中提取到专属的配置文件中。下面以 eslint 为例进行分析: 在初始化项目的时候,如果选择了 eslint 插件,在调用 @vue/cli-plugin-eslint 的 generator 的时候,就会向 package.json 注入 eslintConfig 字段:
module.exports = (api, { config, lintOn = [] }, _, invoking) => {
if (typeof lintOn === 'string') {
lintOn = lintOn.split(',')
}
const eslintConfig = require('../eslintOptions').config(api)
const pkg = {
scripts: {
lint: 'vue-cli-service lint'
},
eslintConfig,
// TODO:
// Move these dependencies to package.json in v4.
// Now in v3 we have to add redundant eslint related dependencies
// in order to keep compatibility with v3.0.x users who defaults to ESlint v4.
devDependencies: {
'babel-eslint': '^10.0.1',
'eslint': '^5.8.0',
'esliint-plugin-vue': '^5.0.0-0'
}
}
const injectEditorConfig = (config) => {
const filePath = api.resolve('.editorconfig')
if (fs.existsSync(filePath)) {
// Append to existing .editorconfig
api.render(files => {
const configPath = path.resolve(__dirname, `./template/${config}/_editorconfig`)
const editorconfig = fs.readFileSync(configPath, 'utf-8')
files['.editorconfig'] += `\n${editorconfig}`
})
} else {
api.render(`./template/${config}`)
}
}
if (config === 'airbnb') {
eslintConfig.extends.push('@vue/airbnb')
Object.assign(pkg.devDependencies, {
'@vue/eslint-config-airbnb': '^4.0.0'
})
injectEditorConfig('airbnb')
} else if (config === 'standard') {
eslintConfig.extends.push('@vue/standard')
Object.assign(pkg.devDependencies, {
'@vue/eslint-config-standard': '^4.0.0'
})
injectEditorConfig('standard')
} else if (config === 'prettier') {
eslintConfig.extends.push('@vue/prettier')
Object.assign(pkg.devDependencies, {
'@vue/eslint-config-prettier': '^4.0.0'
})
// prettier & default config do not have any style rules
// so no need to generate an editorconfig file
} else {
// default
eslintConfig.extends.push('eslint:recommended')
}
api.extendPackage(pkg)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
这是 @vue/cli-plugin-eslint/generator/index.js 中的一部分代码,从代码中可以看出,利用 GeneratorAPI 的 extendPackage 方法向 package.josn 里面注入了 scripts,eslintConfig 以及 devDependencies 字段,另外也会根据选择的 eslint 模式添加对应的依赖和修改对应的配置文件,例如选择了 airbnb 模式,就会向 eslintConfig.extends 添加 @vue/airbnb 配置,并且添加 @vue/eslint-config-airbnb 依赖和修改 .editorconfig 配置文件。此时 项目 package.json 中 eslintConfig 字段内容如下:
{
"eslintConfig": {
"root": true,
"env": {
"node": true
},
"extends": [
"plugin:vue/essential",
"@vue/airbnb"
],
"rules": {},
"parserOptions": {
"parser": "babel-eslint"
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
如果 preset 的 useConfigFiles 为 true ,或者以 Manually 模式初始化 preset 的时候选择 In dedicated config files 存放配置文件:
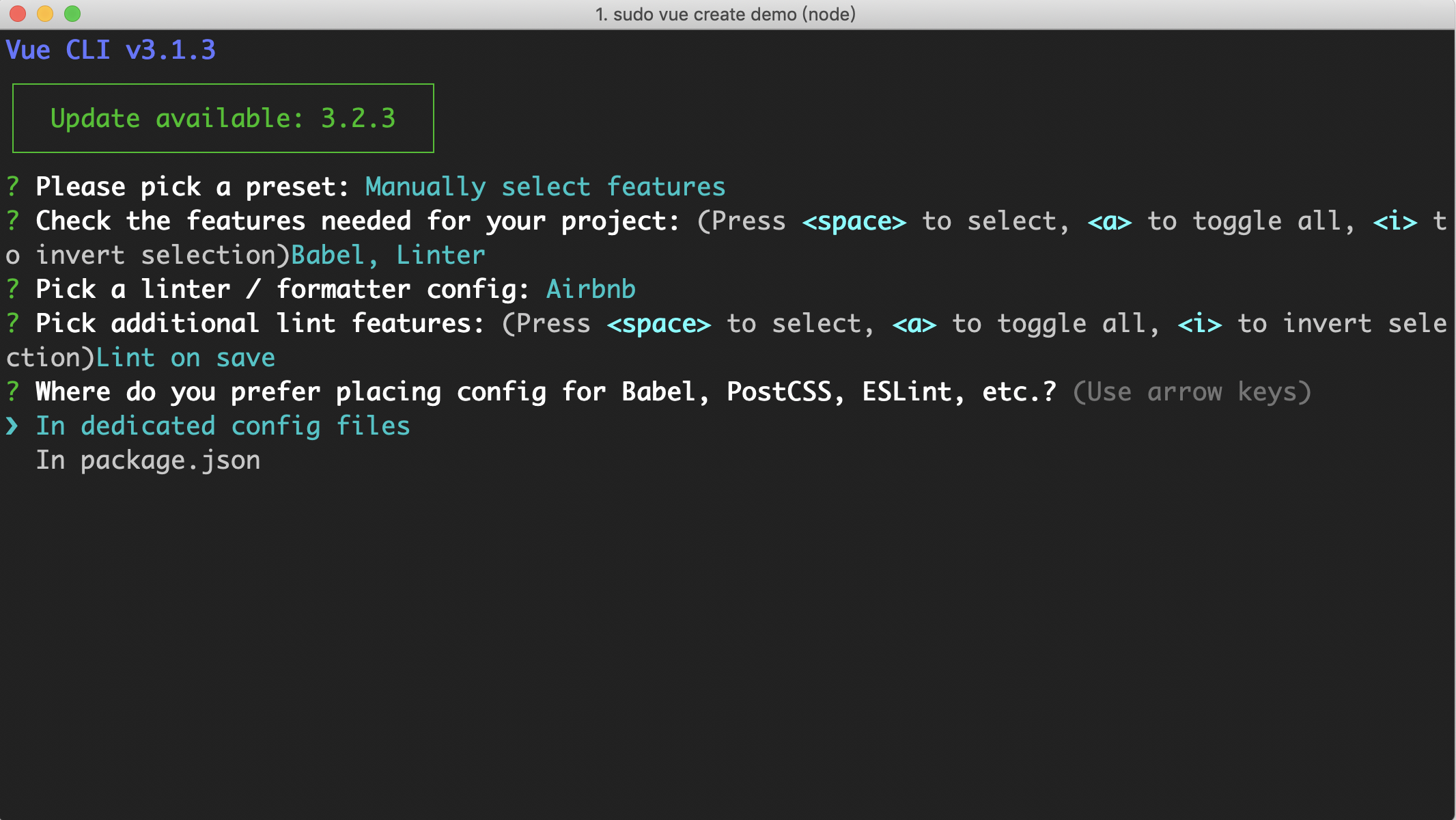
那么 extractConfigFiles 方法就会将 package.json 中 eslintConfig 字段内容提取到 .eslintrc.js 文件中,内存中 .eslintrc.js 内容如下:
module.exports = {
root: true,
env: {
node: true,
},
extends: [
'plugin:vue/essential',
'@vue/airbnb',
],
rules: {
'no-console': process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 'error' : 'off',
'no-debugger': process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 'error' : 'off',
},
parserOptions: {
parser: 'babel-eslint',
},
};
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
extractConfigFiles 方法的具体实现主要是调用 ConfigTransform 实例的 transform 方法,代码实现的比较清晰,各位同学可以自己看下。这里就不做详细 分析了,在配置文件提取完了以后接下来就是执行 resolveFiles 函数了。
# resolveFiles
resolveFiles 主要分为以下三个部分执行:
- fileMiddlewares
- injectImportsAndOptions
- postProcessFilesCbs
fileMiddlewares 里面包含了 ejs render 函数,所有插件调用 api.render 时候只是把对应的渲染函数 push 到了 fileMiddlewares 中,等所有的 插件执行完以后才会遍历执行 fileMiddlewares 里面的所有函数,即在内存中生成模板文件字符串。
injectImportsAndOptions 就是将 generator 注入的 import 和 rootOption 解析到对应的文件中,比如选择了 vuex, 会在 src/main.js 中添加 import store from './store',以及在 vue 根实例中添加 router 选项。
postProcessFilesCbs 是在所有普通文件在内存中渲染成字符串完成之后要执行的遍历回调。例如将 @vue/cli-service/generator/index.js 中的 render 是放在了 fileMiddlewares 里面,而将 @vue/cli-service/generator/router/index.js 中将替换 src/App.vue 文件的方法放在了 postProcessFiles 里面,原因是对 src/App.vue 文件的一些替换一定是发生在 render 函数之后,如果在之前,修改后的 src/App.vue 在之后 render 函数执行时又会被覆盖,这样显然不合理。
# writeFileTree
在提取了配置文件和模板渲染之后调用了 sortPkg 对 package.json 的字段进行了排序并将 package.json 转化为 json 字符串添加到项目的 files 中。 此时整个项目的文件已经在内存中生成好了(在源码中就是对应的 this.files),接下来就调用 writeFileTree 方法将内存中的字符串模板文件生成在磁盘中。到这里 vue create 核心部分 generator 基本上就分析完了,在下一节就分析 vue create 命令剩下的部分。
# 结尾分析
在分析了 Generator 之后可能会有点晕晕的,毕竟 Generator 是 vue create 最核心的部分,而 vue create 又是 @vue/cli 中最核心的部分之一。 没关系,结尾分析这部分比较容易理解,看一下代码就知道结尾做了写什么事了,那就直接看下代码清醒下:
// install additional deps (injected by generators)
log(`📦 Installing additional dependencies...`)
this.emit('creation', { event: 'deps-install' })
log()
if (!isTestOrDebug) {
await installDeps(context, packageManager, cliOptions.registry)
}
// run complete cbs if any (injected by generators)
logWithSpinner('⚓', `Running completion hooks...`)
this.emit('creation', { event: 'completion-hooks' })
for (const cb of createCompleteCbs) {
await cb()
}
// generate README.md
stopSpinner()
log()
logWithSpinner('📄', 'Generating README.md...')
await writeFileTree(context, {
'README.md': generateReadme(generator.pkg, packageManager)
})
// commit initial state
let gitCommitFailed = false
if (shouldInitGit) {
await run('git add -A')
if (isTestOrDebug) {
await run('git', ['config', 'user.name', 'test'])
await run('git', ['config', 'user.email', 'test@test.com'])
}
const msg = typeof cliOptions.git === 'string' ? cliOptions.git : 'init'
try {
await run('git', ['commit', '-m', msg])
} catch (e) {
gitCommitFailed = true
}
}
// log instructions
stopSpinner()
log()
log(`🎉 Successfully created project ${chalk.yellow(name)}.`)
log(
`👉 Get started with the following commands:\n\n` +
(this.context === process.cwd() ? `` : chalk.cyan(` ${chalk.gray('$')} cd ${name}\n`)) +
chalk.cyan(` ${chalk.gray('$')} ${packageManager === 'yarn' ? 'yarn serve' : 'npm run serve'}`)
)
log()
this.emit('creation', { event: 'done' })
if (gitCommitFailed) {
warn(
`Skipped git commit due to missing username and email in git config.\n` +
`You will need to perform the initial commit yourself.\n`
)
}
generator.printExitLogs()
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
可以分为以下4个部分来进行介绍:
- 安装额外依赖
- 执行 createCompleteCbs
- 生成 README.md
- git 初始化提交
- 日志输出
# 安装额外依赖
这里的依赖来源于 preset 的 option,比如选择了 scss css 预处理器,那么就需要额外安装 node-sass 和 sass-loader 两个依赖。
# createCompleteCbs
所有文件都写在磁盘后执行地遍历回调。@vue/cli-plugin-eslint 的 generator 就注入了 createCompleteCbs,源码如下:
// lint & fix after create to ensure files adhere to chosen config
if (config && config !== 'base') {
api.onCreateComplete(() => {
require('../lint')({ silent: true }, api)
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
他的作用就是对生成后的文件进行 lint & fix,保证符合 elsit 所选的配置。
# 生成 README.md
生成 README.md,这里需要注意的一点就是,调用的 generateReadme 函数会根据 package.json 的 script 的字段生成生成对应的 `README.md。
# git 初始化提交
git 初始化提交主要就是调用 shouldInitGit 来判断是否需要 git 初始化提交,如果需要初始化提交就会执行 git add 和 git commmit 命令, 只有在以下这种情况会 git 初始化提交:
- --git: vue create 含有 -g 或者 --git 选项
# 日志输出
插件的 generator 可以利用 GeneratorAPI 暴露的 exitLog 方法在项目输出其他所有的 message 之后输出一些日志。
# 总结
分析了整个 vue create 命令,感受比较明显的两点就是
@vue/cli 3.0比vue-cli 2.0真的复杂的太多了@vue/cli 3.0基于插件的架构做的真心不错
虽然 vue create 真个过程比较复杂,但是从源码一部分一部分地进行分析,会发现真的很复杂,哈哈,开个玩笑😊😊会发现其实整个逻辑十分地清楚, 函数模块化的思想体现的十分明显。看完了源码 vue create 命令总的来说就实例化了2个类,然后各自调了一个方法。当执行 create 命令时会创建一个 Creator 实例, 然后调用其 create 方法。在 create 方法中又会创建一个 Generator 实例,然后再调用其 generator 方法,只是可能方法有点复杂😆😆。 在 @vue/cli 3.0 中使用了大量的 async 函数,这也避免了回调地狱,让代码拥有很高地可读性。
初始化整个项目会交给各个插件去完成。比如核心插件 @vue/cli-service 会渲染整个项目的文件,@vue/cli-plugin-eslint 会进行 eslint 的一些配置, @vue/cli-plugin-unit-jest 插件也会进行一些 jest 的配置,各个功能都会交给对应的插件去完成,而 GeneratorAPI 又允许一个插件的 generator 向 package.json 注入额外的依赖或字段,并向项目中添加文件,这也让插件对整个项目拥有更高地可配置性。
对于 @vue/cli 3.0 基于插件构建的思想可能看了一遍源码不是很熟悉,可以尝试再看一遍,这样你就会慢慢地感受到这种思想,另外就是如果你看了 vue create 的代码后你还是不是很清楚的话,你可以选择用 vue create 创建几个项目,将这个流程和代码的执行顺序结合起来,可能会得到不一样的收获。
# vue add
# add 命令
源码目录: packages/@vue/cli/lib/add.js 。
作用: 在 vue-cli 项目中安装插件并调用其 generator 。
vue add 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js 中:
program
.command('add <plugin> [pluginOptions]')
.description('install a plugin and invoke its generator in an already created project')
.option('--registry <url>', 'Use specified npm registry when installing dependencies (only for npm)')
.allowUnknownOption()
.action((plugin) => {
require('../lib/add')(plugin, minimist(process.argv.slice(3)))
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
从代码中可以看出,vue add 命令接受两个参数:
- plugin: 插件名称,必填。
- registry: 安装插件指定的安装源,只针对于 npm 包管理器,选填。
当执行了 vue add 命令后会加载 @vue/cli/lib/add.js,下面就逐步开始分析。
# 安装插件
vue add 和 vue invoke 两个命令其实有很多相同的地方,即 vue add 包含了 vue invoke 的功能,另外还多了一个插件安装的功能,下面就直接看下代码。
module.exports = (...args) => {
return add(...args).catch(err => {
error(err)
if (!process.env.VUE_CLI_TEST) {
process.exit(1)
}
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
加载 add.js 脚本就会调用 add 函数,接着看 add 函数的代码:
async function add (pluginName, options = {}, context = process.cwd()) {
// special internal "plugins"
// 内部 plugin
if (/^(@vue\/)?router$/.test(pluginName)) { // 匹配 @vue/router,router。 ? 表示匹配前面的子表达式零次或一次
return addRouter(context)
}
if (/^(@vue\/)?vuex$/.test(pluginName)) { // 匹配 @vue/vuex,vuex
return addVuex(context)
}
// 解析插件名称
// full id, scoped short, or default short
// @bar/foo => @bar/vue-cli-plugin-foo
// @vue/foo => @vue/cli-plugin-foo
// foo => vue-cli-plugin-foo
const packageName = resolvePluginId(pluginName)
log()
log(`📦 Installing ${chalk.cyan(packageName)}...`)
log()
const packageManager = loadOptions().packageManager || (hasProjectYarn(context) ? 'yarn' : 'npm')
await installPackage(context, packageManager, options.registry, packageName)
log(`${chalk.green('✔')} Successfully installed plugin: ${chalk.cyan(packageName)}`)
log()
const generatorPath = resolveModule(`${packageName}/generator`, context)
if (generatorPath) {
invoke(pluginName, options, context)
} else {
log(`Plugin ${packageName} does not have a generator to invoke`)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
add 函数并不复杂,主要就是安装插件包,对于 vue-cli 内部一些特殊的"插件",比如 router,vuex,就不会通过包管理器安装,而是直接加载 @vue/cli-service/generator/router 和 @vue/cli-service/generator/vuex,这两个文件也是两个 generator,可以向 package.json 注入额外的依赖或字段,并向项目中添加文件,对于普通的第三方插件,就需要通过包管理器安装了。
安装第三方插件这部分比较重要的就是解析插件的名称,即 resolvePluginId,还是看下 resolvePluginId 的实现:
exports.resolvePluginId = id => {
// already full id
// e.g. vue-cli-plugin-foo, @vue/cli-plugin-foo, @bar/vue-cli-plugin-foo
if (pluginRE.test(id)) { // const pluginRE = /^(@vue\/|vue-|@[\w-]+\/vue-)cli-plugin-/
return id
}
// scoped short
// e.g. @vue/foo, @bar/foo
// @vue/foo => @vue/cli-plugin-foo
// @bar/foo => @bar/vue-cli-plugin-foo
if (id.charAt(0) === '@') {
const scopeMatch = id.match(scopeRE)
if (scopeMatch) {
const scope = scopeMatch[0]
const shortId = id.replace(scopeRE, '')
return `${scope}${scope === '@vue/' ? `` : `vue-`}cli-plugin-${shortId}`
}
}
// default short
// e.g. foo
return `vue-cli-plugin-${id}`
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
看一下代码应该就比较清楚它的作用了,就是将 full id ,scoped short 以及 default short 解析成完整的插件名称。在 vue-cli 官方文档中对插件 的命名有着明确的要求,即命名方式为:vue-cli-plugin-<name>,插件遵循命名约定之后就可以:
- 被
@vue/cli-service发现; - 被其它开发者搜索到;
- 通过
vue add <name>或vue invoke <name>安装下来。
在获取第三方插件名称后,就会调用 installPackage 安装插件包,接下来就是调用插件的 generator 了,调用插件将在下一节分析。调用插件
对于第三方插件安装完成之后,先调用 invoke 方法,该方法实现如下:
async function invoke (pluginName, options = {}, context = process.cwd()) {
delete options._
const pkg = getPkg(context) // 解析 package.json
// attempt to locate the plugin in package.json
const findPlugin = deps => {
if (!deps) return
let name
// official
if (deps[(name = `@vue/cli-plugin-${pluginName}`)]) {
return name
}
// full id, scoped short, or default short
if (deps[(name = resolvePluginId(pluginName))]) {
return name
}
}
const id = findPlugin(pkg.devDependencies) || findPlugin(pkg.dependencies)
if (!id) {
throw new Error(
`Cannot resolve plugin ${chalk.yellow(pluginName)} from package.json. ` +
`Did you forget to install it?`
)
}
const pluginGenerator = loadModule(`${id}/generator`, context)
if (!pluginGenerator) {
throw new Error(`Plugin ${id} does not have a generator.`)
}
// resolve options if no command line options (other than --registry) are passed,
// and the plugin contains a prompt module.
// eslint-disable-next-line prefer-const
let { registry, ...pluginOptions } = options
if (!Object.keys(pluginOptions).length) {
let pluginPrompts = loadModule(`${id}/prompts`, context)
if (pluginPrompts) {
if (typeof pluginPrompts === 'function') {
pluginPrompts = pluginPrompts(pkg)
}
if (typeof pluginPrompts.getPrompts === 'function') {
pluginPrompts = pluginPrompts.getPrompts(pkg)
}
pluginOptions = await inquirer.prompt(pluginPrompts)
}
}
const plugin = {
id,
apply: pluginGenerator,
options: {
registry,
...pluginOptions
}
}
await runGenerator(context, plugin, pkg)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
该方法先调用 findPlugin 判断插件是否安装,接着判断是否有 generator(pluginGenerator),然后就是判断插件是否含有 prompt。如果有则调用 inquirer.prompt 获取插件的 option,并传给其 generator,在完成这些以后,就是 runGenerator。
而对于 vue-cli 内部一些特殊的"插件",比如 router,vuex就直接调用 runGenerator。
如果你看了 vue create 分析部分的 Generator 的话,接下来就比较轻松了。runGenerator 的实质就是构造一个 Generator 实例,并调用其 generate 方法。 如果对 generate 方法还不熟悉的话,可查看下 vue create 部分。 在实例的 generator 方法调用完成之后执行以下命令:
git ls-files --exclude-standard --modified --others
因为插件的 generator 可以通过 GeneratorAPI 暴露的 render 和 extendPackage 方法修改项目的文件,因此通过执行该命令将变化的文件显示在 终端上,这对开发者十分地友好。
# 调用插件
对于第三方插件安装完成之后,先调用 invoke 方法,该方法实现如下:
async function invoke (pluginName, options = {}, context = process.cwd()) {
delete options._
const pkg = getPkg(context) // 解析 package.json
// attempt to locate the plugin in package.json
const findPlugin = deps => {
if (!deps) return
let name
// official
if (deps[(name = `@vue/cli-plugin-${pluginName}`)]) {
return name
}
// full id, scoped short, or default short
if (deps[(name = resolvePluginId(pluginName))]) {
return name
}
}
const id = findPlugin(pkg.devDependencies) || findPlugin(pkg.dependencies)
if (!id) {
throw new Error(
`Cannot resolve plugin ${chalk.yellow(pluginName)} from package.json. ` +
`Did you forget to install it?`
)
}
const pluginGenerator = loadModule(`${id}/generator`, context)
if (!pluginGenerator) {
throw new Error(`Plugin ${id} does not have a generator.`)
}
// resolve options if no command line options (other than --registry) are passed,
// and the plugin contains a prompt module.
// eslint-disable-next-line prefer-const
let { registry, ...pluginOptions } = options
if (!Object.keys(pluginOptions).length) {
let pluginPrompts = loadModule(`${id}/prompts`, context)
if (pluginPrompts) {
if (typeof pluginPrompts === 'function') {
pluginPrompts = pluginPrompts(pkg)
}
if (typeof pluginPrompts.getPrompts === 'function') {
pluginPrompts = pluginPrompts.getPrompts(pkg)
}
pluginOptions = await inquirer.prompt(pluginPrompts)
}
}
const plugin = {
id,
apply: pluginGenerator,
options: {
registry,
...pluginOptions
}
}
await runGenerator(context, plugin, pkg)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
该方法先调用 findPlugin 判断插件是否安装,接着判断是否有 generator(pluginGenerator),然后就是判断插件是否含有 prompt。如果有则调用 inquirer.prompt 获取插件的 option,并传给其 generator,在完成这些以后,就是 runGenerator。
而对于 vue-cli 内部一些特殊的"插件",比如 router,vuex就直接调用 runGenerator。
如果你看了 vue create 分析部分的 Generator 的话,接下来就比较轻松了。runGenerator 的实质就是构造一个 Generator 实例,并调用其 generate 方法。 如果对 generate 方法还不熟悉的话,可查看下 vue create 部分。 在实例的 generator 方法调用完成之后执行以下命令:
git ls-files --exclude-standard --modified --others
因为插件的 generator 可以通过 GeneratorAPI 暴露的 render 和 extendPackage 方法修改项目的文件,因此通过执行该命令将变化的文件显示在 终端上,这对开发者十分地友好。
# 总结
如果了解了 vue create 整个过程,那么相信你对 vue add 命令的代码看起来应该比较轻松,因为 vue add 相当于只是 vue create 中的一部分,vue create 包含了插件的安装以及调用,vue add 命令只是将此功能分离了出来。
有个消息就是,接下来分析的 vue invoke 命令其实是 vue add 命名去掉了插件包安装的那一部分,所以同学们都懂噻😁😁。
扶我起来,我还能学习,接下来就开始 vue invoke 命令的分析。
# vue invoke
# invoke 命令
源码目录: packages/@vue/cli/lib/invoke.js 。
作用: 在 vue-cli 项目中调用插件的 generator 。
vue invoke 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js 中:
program
.command('invoke <plugin> [pluginOptions]')
.description('invoke the generator of a plugin in an already created project')
.option('--registry <url>', 'Use specified npm registry when installing dependencies (only for npm)')
.allowUnknownOption()
.action((plugin) => {
require('../lib/invoke')(plugin, minimist(process.argv.slice(3)))
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
从代码中可以看出,vue invoke 命令接受两个参数:
- plugin: 插件名称,必填。
- registry: 安装插件指定的安装源,只针对于 npm 包管理器,选填。
当执行了 vue add 命令时会加载 @vue/cli/lib/invoke.js,对于插件的调用在 vue add 命令中已经分析了,这里就不做介绍。vue add 本身就包含了 vue invoke 的功能,而vue invoke 只是将插件调用的功能分离出了。在某些场景下该功能十分方便,比如当你执行 vue add 安装并调用了 一个插件的 generator 之后,你想要更改这个插件配置,那么此时只需要执行 vue invoke 调用插件的 generator 修改配置即可。
# vue inspect
# inspect 命令
源码目录: packages/@vue/cli/lib/inspect.js 。
作用: 审查一个 Vue CLI 项目的 webpack config 。
vue inspect 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js 中:
program
.command('inspect [paths...]')
.description('inspect the webpack config in a project with vue-cli-service')
.option('--mode <mode>')
.option('--rule <ruleName>', 'inspect a specific module rule')
.option('--plugin <pluginName>', 'inspect a specific plugin')
.option('--rules', 'list all module rule names')
.option('--plugins', 'list all plugin names')
.option('-v --verbose', 'Show full function definitions in output')
.action((paths, cmd) => {
require('../lib/inspect')(paths, cleanArgs(cmd))
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
当执行了 vue inspect 命令时会加载 @vue/cli/lib/inspect.js,那么接下来分析 inspect.js 代码。
module.exports = function inspect (paths, args) {
const cwd = process.cwd()
let servicePath
try {
servicePath = resolve.sync('@vue/cli-service', { basedir: cwd }) // cwd/node_modules/@vue/cli-service/lib/Service.js
} catch (e) {
const { error } = require('@vue/cli-shared-utils')
error(
`Failed to locate @vue/cli-service.\n` +
`Note that \`vue inspect\` is an alias of \`vue-cli-service inspect\`\n` +
`and can only be used in a project where @vue/cli-service is locally installed.`
)
process.exit(1)
}
const binPath = path.resolve(servicePath, '../../bin/vue-cli-service.js') // cwd/node_modules/@vue/cli-service/bin/vue-cli-service.js
if (fs.existsSync(binPath)) {
execa('node', [
binPath,
'inspect',
...(args.mode ? ['--mode', args.mode] : []),
...(args.rule ? ['--rule', args.rule] : []),
...(args.plugin ? ['--plugin', args.plugin] : []),
...(args.rules ? ['--rules'] : []),
...(args.plugins ? ['--plugins'] : []),
...(args.verbose ? ['--verbose'] : []),
...paths
], { cwd, stdio: 'inherit' })
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
这段代码比较好理解,作用就是获取 @vue/cli-service 的执行文件路径,然后执行其 inspect 命令。也就是说 vue inspect 命令实际执行的是 vue-cli-service inspect 命令,相关分析可查看 cli-service 内置插件 inspect (opens new window)。
# vue serve
# serve 命令
源码目录: packages/@vue/cli-service-global 。
作用: 在开发环境模式下零配置为 .js 或 .vue 文件启动一个服务器 。
vue serve 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js 中:
program
.command('serve [entry]')
.description('serve a .js or .vue file in development mode with zero config')
.option('-o, --open', 'Open browser')
.option('-c, --copy', 'Copy local url to clipboard')
.action((entry, cmd) => {
loadCommand('serve', '@vue/cli-service-global').serve(entry, cleanArgs(cmd))
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
代码写的很清楚了,当执行 vue serve 命令时会执行 @vue/cli-service-global 的 serve 方法,那就直接看 serve 方法源码:
exports.serve = (_entry, args) => {
const { context, entry } = resolveEntry(_entry)
createService(context, entry).run('serve', args)
}
2
3
4
首先调用 resolveEntry 获取入口文件 entry,和当前工作目录 context,看 resolveEntry 函数代码:
function resolveEntry (entry) {
const context = process.cwd()
entry = entry || findExisting(context, [
'main.js',
'index.js',
'App.vue',
'app.vue'
])
if (!entry) {
console.log(chalk.red(`Failed to locate entry file in ${chalk.yellow(context)}.`))
console.log(chalk.red(`Valid entry file should be one of: main.js, index.js, App.vue or app.vue.`))
process.exit(1)
}
if (!fs.existsSync(path.join(context, entry))) {
console.log(chalk.red(`Entry file ${chalk.yellow(entry)} does not exist.`))
process.exit(1)
}
return {
context,
entry
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
如果 vue serve 命令中含有 --entry 参数,那么入口文件就取参数中的文件,否则会依次判断在当前工作目录是否存在 main.js,index.js,App.vue,app.vue, 文件,只要存在就会返回,针对于参数中含有 entry 的情形还会判断 entry 文件是否存在,如果存在则将当前工作目录和入口文件一起返回。
接下来就创建了一个 Service 实例,并执行其 run 方法,如果之前看了 cli-service (opens new window) 部分的话,我相信到这里就应该就非常熟悉了,相当于就执行了 vue-cli-service serve 命令。还是看下在 createService 中发生了什么:
function createService (context, entry, asLib) {
return new Service(context, {
projectOptions: {
compiler: true,
lintOnSave: true
},
plugins: [
babelPlugin,
eslintPlugin,
globalConfigPlugin(context, entry, asLib)
]
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
createService 主要工作就是实例化一个 Service,并且初始化了 projectOptions 和 plugins,看一下 globalConfigPlugin 的代码:
module.exports = function createConfigPlugin (context, entry, asLib) {
return {
id: '@vue/cli-service-global-config',
apply: (api, options) => {
api.chainWebpack(config => {
// some code ...
})
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
这就是一个 service 插件,主要进行了 webpack 的一些配置。在此之后就调用了实例的 run 方法,执行了 vue-cli-service serve 命令,相关分析可查看 cli-service 内置插件 serve (opens new window)。
# vue build
# build 命令
源码目录: packages/@vue/cli-service-globa 。
作用: 在生产环境模式下零配置构建一个 .js 或 .vue 文件 。
vue build 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js 中:
program
.command('build [entry]')
.description('build a .js or .vue file in production mode with zero config')
.option('-t, --target <target>', 'Build target (app | lib | wc | wc-async, default: app)')
.option('-n, --name <name>', 'name for lib or web-component mode (default: entry filename)')
.option('-d, --dest <dir>', 'output directory (default: dist)')
.action((entry, cmd) => {
loadCommand('build', '@vue/cli-service-global').build(entry, cleanArgs(cmd))
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
与 vue serve 命令类似,当执行 vue build 命令时会执行 @vue/cli-service-global 的 build 方法,那就直接看 build 方法源码:
exports.build = (_entry, args) => {
const { context, entry } = resolveEntry(_entry)
const asLib = args.target && args.target !== 'app'
if (asLib) {
args.entry = entry
}
createService(context, entry, asLib).run('build', args)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
基本上和 vue serve 命令一样,只是针对于构建目标为 lib ,wc 以及 wc-async 时为 build 命令添加了 entry 参数,防止找不到构建入口。因为当不指定 构建目标入口时,默认为 src/App.vue,那么如果 vue build 命令不指定 entry 参数,就很容易出现找不到构建入口的情形。
# vue ui
# ui 命令
源码目录: packages/@vue/cli/lib/ui.js 。
作用: 以图形化界面创建和管理项目。
vue ui 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/ui.js 中:
program
.command('ui')
.description('start and open the vue-cli ui')
.option('-H, --host <host>', 'Host used for the UI server (default: localhost)')
.option('-p, --port <port>', 'Port used for the UI server (by default search for available port)')
.option('-D, --dev', 'Run in dev mode')
.option('--quiet', `Don't output starting messages`)
.option('--headless', `Don't open browser on start and output port`)
.action((cmd) => {
checkNodeVersion('>=8.6', 'vue ui')
require('../lib/ui')(cleanArgs(cmd))
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
和其它 vue 命令一样,从这里可以简单查看 ui 命令的一些参数,其中包括 host 配置,端口配置以及在什么模式下运行等等,ui 命令的回调 action 会加载 ui.js,但在分析 ui.js 之前先整体上分析 vue ui 命令,以及其中涉及到的一些知识。
# 整体分析
ui 命令旨在通过 GUI 的形式对 vue 项目进行管理,可以说是 vue-cli3.0 中的除了插件系统后的又一大新特性,那么整个 ui 系统是怎么运行起来的呢,可以大致的分为两部分进行分析,server 端和 client 端。server 端主要使用了 apollo-server (opens new window) 与 express (opens new window),以 GraphQL (opens new window) API 查询语言来实现数据的查询,变更以及订阅。而 client 端在 ui 方面使用了自家的 @vue/ui (opens new window),另外在项目中还集成了vue-apollo (opens new window)。
先从 cli 官网搬一张图来整体感受下 vue ui:
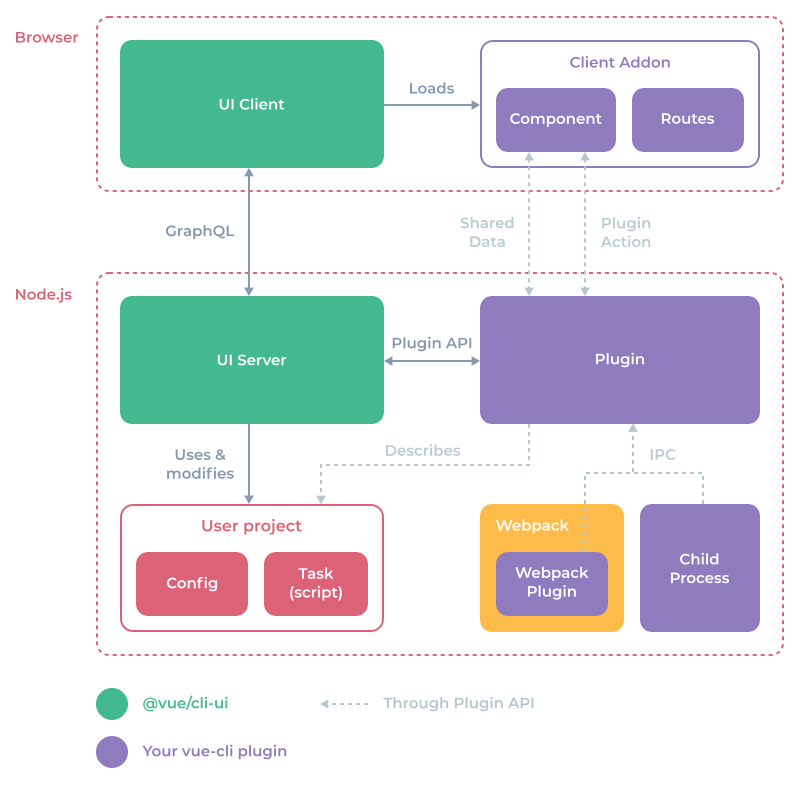
这张图是 vue ui 的整体架构,如果现在不是很清楚里面里面涉及的知识的话,不要慌,可以在了解完 ui 命令后再来回看一下。
除此之外,还需要了解以下这些知识:
- GraphQL (opens new window):API 查询语言
- apollo-server (opens new window): nodejs上构建grqphql服务端的web中间件,支持express,koa ,hapi等框架。
- vue-apollo (opens new window):在 vue 项目中集成 GraphQL
- express (opens new window):Node.js Web 应用程序框架
接下来就从 server 端和 client 端进行分析。
# server 分析
先看下 ui 命令加载的 lib/ui.js 内容:
async function ui (options = {}, context = process.cwd()) {
const host = options.host || 'localhost'
// some code ...
if (!options.quiet) log(`🚀 Starting GUI...`)
const opts = {
host, // 域名
port, // 端口
graphqlPath: '/graphql',
subscriptionsPath: '/graphql', // 订阅
enableMocks: false, // 是否模拟数据
enableEngine: false, // Apollo Engine
cors: '*',
timeout: 1000000,
quiet: true,
paths: {
typeDefs: require.resolve('@vue/cli-ui/apollo-server/type-defs.js'), // schema
resolvers: require.resolve('@vue/cli-ui/apollo-server/resolvers.js'), // resolvers
context: require.resolve('@vue/cli-ui/apollo-server/context.js'), // 可以向 resolvers 注入上下文对象
pubsub: require.resolve('@vue/cli-ui/apollo-server/pubsub.js'), // 订阅
server: require.resolve('@vue/cli-ui/apollo-server/server.js'), // express 服务 e.g. express.static
directives: require.resolve('@vue/cli-ui/apollo-server/directives.js') // schema 指令
}
}
server(opts, () => {
// server cb()
// some code ...
})
}
module.exports = (...args) => {
return ui(...args).catch(err => {
error(err)
if (!process.env.VUE_CLI_TEST) {
process.exit(1)
}
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
上面是 lib/ui.js 的部分代码,主要就是获取 opts,然后执行 @vue/cli-ui 的 server 方法。在 opts 中需要注意的就是 opts.path , 它定义一些变量的路径,具体作用如下:
- typeDefs: GraphQL Schema,用来定义 GraphQL 数据模型
- resolvers: 用于解析 GraphQL Query 获取的数据
- context:可以向 resolvers 注入上下文对象
- pubsub:GraphQL 订阅
- server:express 服务,利用 app.use 注册中间件
- directives: GraphQL 指令, @include,@skip
接下来看服务端启动的代码,代码目录在 vue-cli-plugin-apollo/graphql-server/index.js 中,简单看下部分代码:
// 创建基于 express 的 GraphQL server
// apollo-server-express 是由 Apollo 提供在 express 环境下实现 GraphQL 的库
module.exports = (options, cb = null) => {
// some code ...
// Express app
const app = express()
if (options.typescript) require('ts-node/register/transpile-only')
// Customize those files
let typeDefs = load(options.paths.typeDefs) // GraphQL schema
const resolvers = load(options.paths.resolvers) // GraphQL resolvers
// ...
let apolloServerOptions = {
typeDefs,
resolvers,
schemaDirectives,
dataSources,
tracing: true,
cacheControl: true,
engine: !options.integratedEngine,
// Resolvers context from POST
context: async ({ req, connection }) => {
let contextData
try {
if (connection) {
contextData = await autoCall(context, { connection })
} else {
contextData = await autoCall(context, { req })
}
} catch (e) {
console.error(e)
throw e
}
contextData = Object.assign({}, contextData, { pubsub })
return contextData
},
// Resolvers context from WebSocket
subscriptions: {
path: options.subscriptionsPath,
onConnect: async (connection, websocket) => {
let contextData = {}
try {
contextData = await autoCall(context, {
connection,
websocket,
})
contextData = Object.assign({}, contextData, { pubsub })
} catch (e) {
console.error(e)
throw e
}
return contextData
},
},
}
// ...
// Apollo Server
const server = new ApolloServer(apolloServerOptions)
// Express middleware
// 通过 applyMiddleware() 作为 app 来传递它,来添加 Apollo Server 的中间件
server.applyMiddleware({
app,
path: options.graphqlPath,
cors: options.cors,
// gui: {
// endpoint: graphqlPath,
// subscriptionEndpoint: graphqlSubscriptionsPath,
// },
})
// Start server
const httpServer = http.createServer(app)
httpServer.setTimeout(options.timeout)
server.installSubscriptionHandlers(httpServer)
httpServer.listen({
host: options.host || 'localhost',
port: options.port,
}, () => {
if (!options.quiet) {
console.log(`✔️ GraphQL Server is running on ${chalk.cyan(`http://localhost:${options.port}${options.graphqlPath}`)}`)
if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && !process.env.VUE_CLI_API_MODE) {
console.log(`✔️ Type ${chalk.cyan('rs')} to restart the server`)
}
}
cb && cb()
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
以上是 server 的部分代码,主要作用是利用 apollo-server 在 nodejs 上构建 grqphql 服务端的 web 中间件,由于 server 端是 express 环境, 因此使用了 npm 包 apollo-server-express,到这里,服务端就启动起来了。
vue-cli-plugin-apollo
启动 server 使用了 vue-cli-plugin-apollo (opens new window)插件, 它是 vue-apollo (opens new window) 的 cli 插件,但与 vue-apollo 相比,它又有更多的新特性,比如集成了 apollo-server 以及包含一些 vue apollo 例子等等。
# client 分析
client 端可以看作是一个 vue 项目,它是通过 vue 组件构成,在 ui 方面使用了自家的 @vue/ui (opens new window),由于 server 端采用了 graphql,因此 client 端使用了 vue-apollo (opens new window),这样可以利用其提供的 API 和组件高效方便地使用 graphql 进行查询,变更以及订阅。
client 端的内容非常多,从项目创建到项目配置、运行以及打包发布,涉及到的代码很多,但大部分的流程基本上一致,这就不会一一做分析了,会选择导入项目这部分来分析,因为 ui 命令也是基于插件机制的,而导入项目的时候会涉及到插件加载以及利用 PluginAPI 增强项目的配置和任务,下面就开始分析项目导入的整个过程。
源码目录
vue ui 运行的客户端是要打包压缩过的代码,目录为 @vue/cli-ui/dist,通过以下代码设置了静态资源(文件)目录,访问 localhost:8000 则指向 @vue/cli-ui/dist/index.html,从而启动了 client 端,对应的源码目录为 @vue/cli-ui/src。
app.use(express.static(distPath, { maxAge: 0 }))
# importProject
导入项目的组件为 @vue/cli-ui/src/components/project-manager/ProjectSelect.vue,部分代码如下
<div class="actions-bar center">
<VueButton
icon-left="unarchive"
:label="$route.query.action || $t('org.vue.views.project-select.buttons.import')"
class="big primary import-project"
:disabled="folderCurrent && !folderCurrent.isPackage"
:loading="busy"
@click="importProject()"
/>
</div>
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
这是不是看着就熟悉了,接着看 importProject 方法:
async importProject (force = false) {
this.showNoModulesModal = false
this.busy = true
await this.$nextTick()
try {
await this.$apollo.mutate({
mutation: PROJECT_IMPORT,
variables: {
input: {
path: this.folderCurrent.path,
force
}
}
})
this.$router.push({ name: 'project-home' })
} catch (e) {
if (e.graphQLErrors && e.graphQLErrors.some(e => e.message === 'NO_MODULES')) {
this.showNoModulesModal = true
}
this.busy = false
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
代码写的比较明了,当执行 importProject 时候会利用 vue-apollo 提供的 this.$apollo.mutate() 来发送一个 GraphQL 变更,从而改变服务端的数据,接下来就看服务端的 Mutation: projectImport。
# Mutation
处理 projectImport 变更的代码目录在 @vue/cli-ui/apollo-server/schema/project.js 中,代码如下:
exports.resolvers = {
Project: { // ...
},
Query: { // ...
},
Mutation: {
// ...
projectImport: (root, { input }, context) => projects.import(input, context),
// ...
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
接着看 projects.import,代码目录在 @vue/cli-ui/apollo-server/connectors/projects.js 中,代码如下:
async function importProject (input, context) { // 导入项目,执行 projectImport mutate
if (!input.force && !fs.existsSync(path.join(input.path, 'node_modules'))) { // 强制导入没有 node_modules 的情形
throw new Error('NO_MODULES')
}
const project = {
id: shortId.generate(), // shortId
path: input.path, // 导入项目的路径
favorite: 0,
type: folders.isVueProject(input.path) ? 'vue' : 'unknown' // 是否为 vue 项目
}
const packageData = folders.readPackage(project.path, context)
project.name = packageData.name
context.db.get('projects').push(project).write() // 将 project 信息存在本地的 db 中 ( lowdb 实现 )
return open(project.id, context)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
importProject 方法的作用就是获取导入项目的信息,并利用 lowdb (opens new window) 将数据存储在本地(~/.vue-cli-ui/db.json),接着执行 open 方法加载插件。
# 插件加载
async function open (id, context) {
const project = findOne(id, context)
// ...
cwd.set(project.path, context) // process.env.VUE_CLI_CONTEXT
// Reset locales
locales.reset(context)
// Load plugins
// 加载插件
await plugins.list(project.path, context)
// ...
return project
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
以上为 open 方法的部分代码,比较核心的就是 await plugins.list(project.path, context),接着看
async function list (file, context, { resetApi = true, lightApi = false, autoLoadApi = true } = {}) {
let pkg = folders.readPackage(file, context)
let pkgContext = cwd.get()
// Custom package.json location
if (pkg.vuePlugins && pkg.vuePlugins.resolveFrom) { // 加载其他文件夹里的 package.json
pkgContext = path.resolve(cwd.get(), pkg.vuePlugins.resolveFrom)
pkg = folders.readPackage(pkgContext, context)
}
pkgStore.set(file, { pkgContext, pkg })
let plugins = []
// package.json 中 devDependencies,dependencies 插件
plugins = plugins.concat(findPlugins(pkg.devDependencies || {}, file))
plugins = plugins.concat(findPlugins(pkg.dependencies || {}, file))
// Put cli service at the top
const index = plugins.findIndex(p => p.id === CLI_SERVICE)
if (index !== -1) {
const service = plugins[index]
plugins.splice(index, 1)
plugins.unshift(service)
}
pluginsStore.set(file, plugins)
log('Plugins found:', plugins.length, chalk.grey(file))
if (resetApi || (autoLoadApi && !pluginApiInstances.has(file))) {
await resetPluginApi({ file, lightApi }, context)
}
return plugins
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
list 方法首先会获取 package.json 里 devDependencies 和 dependencies 字段中的 UI 插件,接着执行 resetPluginApi 函数调用 UI 插件的 API,resetPluginApi 方法部分代码如下:
function resetPluginApi ({ file, lightApi }, context) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// ...
// Cyclic dependency with projects connector
setTimeout(async () => {
// ...
pluginApi = new PluginApi({
plugins,
file,
project,
lightMode: lightApi
}, context)
pluginApiInstances.set(file, pluginApi)
// Run Plugin API
// 默认的插件 suggest,task,config,widgets
runPluginApi(path.resolve(__dirname, '../../'), pluginApi, context, 'ui-defaults')
// devDependencies dependencies 插件
plugins.forEach(plugin => runPluginApi(plugin.id, pluginApi, context))
// Local plugins
// package.json 中 vuePlugins.ui 插件
const { pkg, pkgContext } = pkgStore.get(file)
if (pkg.vuePlugins && pkg.vuePlugins.ui) {
const files = pkg.vuePlugins.ui
if (Array.isArray(files)) {
for (const file of files) {
runPluginApi(pkgContext, pluginApi, context, file)
}
}
}
// Add client addons
pluginApi.clientAddons.forEach(options => {
clientAddons.add(options, context)
})
// Add views
for (const view of pluginApi.views) {
await views.add({ view, project }, context)
}
// Register widgets
for (const definition of pluginApi.widgetDefs) {
await widgets.registerDefinition({ definition, project }, context)
}
// callHook ...
// Load widgets for current project
widgets.load(context)
resolve(true)
})
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
resetPluginApi 方法主要利用函数 runPluginApi 执行所有 UI 插件的 PluginAPI,这里的 UI 插件来源主要有三部分组成:
- 内置 UI 插件:包括了配置插件,建议插件(vue-router,vuex),任务插件以及看板部分的 widget 插件
- package.json UI 插件:项目中依赖的 UI 插件,可以通过 vuePlugins.resolveFrom 指定 package.json 位置
- vuePlugins.ui: package.json 中 vuePlugins 字段中的 UI 插件,这样可以直接访问插件 API
还是按照流程继续看下 runPluginApi 的核心代码:
function runPluginApi (id, pluginApi, context, filename = 'ui') {
// ...
try {
module = loadModule(`${id}/${filename}`, pluginApi.cwd, true)
} catch (e) {}
if (module) {
if (typeof module !== 'function') { } else {
pluginApi.pluginId = id
try {
module(pluginApi)
log('Plugin API loaded for', name, chalk.grey(pluginApi.cwd))
} catch (e) {}
pluginApi.pluginId = null
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
首先尝试加载 UI 插件的 ui.js (也可以ui/index.js),对于内置的 UI 插件,则加载 id/ui-defaults/index.js,加载完成以后则执行其 PluginAPI,PluginAPI (opens new window) 提供了很多的方法来增强项目的配置和任务以及分享数据和在进程间进行通信,具体查看官方文档,PluginAPI 在整个插件机制中是十分重要的一部分。在加载完所有 UI 插件后,则加载 PluginAPI 实例中 addons, views 和 widgetDefs 注册的 vue 组件。以 client addons 为例简单看下:
function add (options, context) {
if (findOne(options.id)) remove(options.id, context)
addons.push(options)
context.pubsub.publish(channels.CLIENT_ADDON_ADDED, {
clientAddonAdded: options
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
当执行 clientAddons.add(options, context) 会发布一个订阅,而 client 端在 cli-ui/src/components/client-addon/ClientAddonLoader.vue 中启用了 client_addon_added 订阅:
apollo: {
clientAddons: {
query: CLIENT_ADDONS,
fetchPolicy: 'no-cache',
manual: true,
result ({ data: { clientAddons }, stale }) {
if (!stale) {
clientAddons.forEach(this.loadAddon)
this.$_lastRead = Date.now()
}
}
},
$subscribe: {
clientAddonAdded: {
query: CLIENT_ADDON_ADDED,
result ({ data }) {
if (this.$_lastRead && Date.now() - this.$_lastRead > 1000) {
this.loadAddon(data.clientAddonAdded)
}
}
}
}
},
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
当在 server 端发布了一个订阅后,client 端会就是执行 loadAddon 从而加载客户端 addon 包,loadAddon 代码如下:
loadAddon (addon) {
// eslint-disable-next-line no-console
console.log(`[UI] Loading client addon ${addon.id} (${addon.url})...`)
const script = document.createElement('script')
script.setAttribute('src', addon.url)
document.body.appendChild(script)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
loadAddon 方法通过 <script> 标签的方式将客户端 addon 包引入,view,widgets 这就暂不分析了,可自行查看下。 在 UI 插件加载完毕后,会执行对应的钩子回调 callHook。
if (projectId !== project.id) {
callHook({
id: 'projectOpen',
args: [project, projects.getLast(context)],
file
}, context)
} else {
callHook({
id: 'pluginReload',
args: [project],
file
}, context)
// View open hook
const currentView = views.getCurrent()
if (currentView) views.open(currentView.id)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
最后再加载当前项目的 widgets,到这里加载插件,即下面这段代码执行完毕:
await plugins.list(project.path, context)
接着看 open 函数剩下的部分:
// Date
context.db.get('projects').find({ id }).assign({
openDate: Date.now()
}).write()
// Save for next time
context.db.set('config.lastOpenProject', id).write()
log('Project open', id, project.path)
return project
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
这段代码的作用就是将当前项目的信息存储在本地 db 中作为下次默认打开,执行到这里打开项目 importProject 的整个过程就分析完了。
# 总结
vue-cli 3.0 中 UI 系统应该是一个亮点,通过完整的 GUI 形式来管理整个 vue 项目,ui 命令涉及的知识应该算是比较多的,在刚开始分析的时候由于对 graphql 了解的比较少,对代码的整个运行不是很清楚,在了解 graphql 以及 vue-apollo 之后,对于 ui 命令的代码就有了思路。ui 系统其实也是基于插件机制的,比较核心的就是 PluginAPI,通过分析打开项目 importProject 可以比较清楚的了解 UI 插件是如何利用 PluginAPI 来增强项目的配置和任务,如果对 PluginAPI 不是很清楚的话可以看下 packages/@vue/cli-ui-addon-webpack 代码,cli-ui-addon-webpack 创建了项目任务模块中 webpack 客户端 addon(serve,build)。
vue-cli 3.0 中核心部分是 Creator (opens new window) 和 Service (opens new window), 可在 create 部分可 vue-cli-service 部分查看具体分析 ,ui 命令是一个 GUI 的形式,在后台运行的还是 nodejs 代码,比如点击创建项目的时候还是会引入@vue/cli/lib/Creator 并执行,点击任务看板中的 “运行” 实质执行的是 vue-cli-service serve 命令。
# vue init
# init 命令
源码目录: packages/@vue/cli-init/index.js 。
作用: 下载远程模板并生成项目 。
相关说明: vue init 命令主要是 2.x 版本使用,但在 3.0中还是将其保留,3.0 推荐使用 vue create 。
vue init 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js 中:
program
.command('init <template> <app-name>')
.description('generate a project from a remote template (legacy API, requires @vue/cli-init)')
.option('-c, --clone', 'Use git clone when fetching remote template')
.option('--offline', 'Use cached template')
.action(() => {
loadCommand('init', '@vue/cli-init')
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
vue init 命令需要输入模版的名称(template)以及 项目名称(app-name),而且都为必填。模版名称可以是官方的模板,官方模版 (opens new window) 包含了 webpack (opens new window),pwa (opens new window),webpack-simple (opens new window),simple (opens new window),browserify (opens new window),browserify-simple (opens new window) 这 6 种模板。当然支持自定义 Github 模板,比如初始化 mpvue-quickstart的命令如下:
vue init mpvue/mpvue-quickstart my-project
mpvue/mpvue-quickstart (opens new window) 中的 template 就为mpvue-quickstart 的内容。
另外 option 包含了 -c 和 -offline,这两个参数的作用为:
- -c:当利用
download-git-repo获取模版的时候采用git clone下载而不是http 下载,默认采用 http 下载。 - --offline:使用缓存的 template 模板,位于
~/.vue-templates目录下面。
当执行 vue-init 命令的时候 loadCommand 函数会加载 @vue/cli-init 模块,这也是为什么当你安装了 @vue/cli,但没有安装 @vue/cli-init 的时候执行 vue init <template> <app-name> 会有以下的提示:
接下来我们就开始分析@vue/cli-init 模块做了什么事情。
# @vue/cli-init 分析
@vue/cli-init 的源码很简单,如下:
const execa = require('execa')
const binPath = require.resolve('vue-cli/bin/vue-init')
execa(
binPath,
process.argv.slice(process.argv.indexOf('init') + 1),
{ stdio: 'inherit' }
)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
对,你没有看错,这就是 @vue/cli-init 的源码。这段代码引入了 execa (opens new window),execa 是可以调用 shell 和本地外部程序的 javascript 封装,会启动子进程执行。支持多操作系统,包括 windows。如果父进程退出,则生成的全部子进程都被杀死。对应在这里就会启动一个子线程去执行 vue-cli/bin/vue-init 脚本,那么 vue-cli/bin/vue-init 又是什么脚本?其实就是 vue-cli 2.x 中对应 vue init 的脚本(vue cli 3.0 中 vue init 命令的源码就是加载 vue-cli 2.x 中的 vue init 命令)。
那么接下来就开始分析 vue-cli 2.x 中 init 命令的源码。
# vue-cli 2.x init 分析
当开始执行 vue-cli-init/bin/vue-init 的代码时,会进入这个判断:
if (inPlace || exists(to)) {
inquirer.prompt([{
type: 'confirm',
message: inPlace
? 'Generate project in current directory?'
: 'Target directory exists. Continue?',
name: 'ok'
}]).then(answers => {
if (answers.ok) {
run()
}
}).catch(logger.fatal)
} else {
run()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
这段代码的作用是:
- 如果没有填写 app-name ,则默认在当前目录生成模版。 在 vue-cli 3.0 中 app-name 为必填,不过在 vue-cli 2.x 中为非必填。
- 如果当前目录有与 app-name 重名的,是否要继续。
然后根据用户的回答来判断是否执行 run 函数,对应的代码如下:
function run () {
// check if template is local
if (isLocalPath(template)) {
const templatePath = getTemplatePath(template)
if (exists(templatePath)) {
generate(name, templatePath, to, err => {
if (err) logger.fatal(err)
console.log()
logger.success('Generated "%s".', name)
})
} else {
logger.fatal('Local template "%s" not found.', template)
}
} else {
checkVersion(() => {
if (!hasSlash) {
// use official templates
const officialTemplate = 'vuejs-templates/' + template
if (template.indexOf('#') !== -1) {
downloadAndGenerate(officialTemplate)
} else {
if (template.indexOf('-2.0') !== -1) {
warnings.v2SuffixTemplatesDeprecated(template, inPlace ? '' : name)
return
}
// warnings.v2BranchIsNowDefault(template, inPlace ? '' : name)
downloadAndGenerate(officialTemplate)
}
} else {
downloadAndGenerate(template)
}
})
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
run 函数作用如下:
- 是否需要从缓存中读取模版并生成
- 下载官方模板还是自定义模板
如果按照正常流程来的话(方便下一步描述,不然 return 了就没得什么分析的了)会执行 downloadAndGenerate 函数,总算到了核心部分了,来看一下 downloadAndGenerate 函数的代码:
function downloadAndGenerate (template) {
const spinner = ora('downloading template')
spinner.start()
// Remove if local template exists
if (exists(tmp)) rm(tmp)
download(template, tmp, { clone }, err => {
spinner.stop()
if (err) logger.fatal('Failed to download repo ' + template + ': ' + err.message.trim())
generate(name, tmp, to, err => {
if (err) logger.fatal(err)
console.log()
logger.success('Generated "%s".', name)
})
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
downloadAndGenerate 函数其实很简洁,就是利用 download-git-repo (opens new window) 从 Github 拉取模板,然后生成在 ~/.vue-templates目录下面,之后会又会调用 generate 函数将~/.vue-templates 目录下面的模板来生成文件。
到这里也许有些朋友会问:直接把模板下载下来放在 /app-name 目录下面不就可以了?如果是静态的模板的的确可以这么做,但是在 vue-cli 初始化一个项目的过程中会询问你 Project name, Project description 以及是否需要安装 vue-router等等,最后会根据你的回答来生成对应的文件,所以直接将静态的模板放在 /app-name 目录显然不行,因此调用generate 函数动态地生成模板。
其实分析到这里就会发现 vue-cli 会将一个功能拆分为多个模块来写,这中模块化的思想是非常值得学习的,好了,下一节开始分析 generate 函数的实现,这也是 init 命令中最核心的部分。
# generate 函数分析
首先直接看代码:
module.exports = function generate (name, src, dest, done) {
const opts = getOptions(name, src) // 获取配置信息
const metalsmith = Metalsmith(path.join(src, 'template')) // 定义 Metalsmith 工作目录 ~/.vue-templates`
const data = Object.assign(metalsmith.metadata(), { // 定义一些全局变量,这样可以在 layout-files 中使用
destDirName: name,
inPlace: dest === process.cwd(),
noEscape: true
})
opts.helpers && Object.keys(opts.helpers).map(key => {
Handlebars.registerHelper(key, opts.helpers[key])
})
const helpers = { chalk, logger }
if (opts.metalsmith && typeof opts.metalsmith.before === 'function') {
opts.metalsmith.before(metalsmith, opts, helpers)
}
metalsmith.use(askQuestions(opts.prompts))
.use(filterFiles(opts.filters))
.use(renderTemplateFiles(opts.skipInterpolation))
if (typeof opts.metalsmith === 'function') {
opts.metalsmith(metalsmith, opts, helpers)
} else if (opts.metalsmith && typeof opts.metalsmith.after === 'function') {
opts.metalsmith.after(metalsmith, opts, helpers)
}
metalsmith.clean(false)
.source('.') // start from template root instead of `./src` which is Metalsmith's default for `source`
.destination(dest)
.build((err, files) => {
done(err)
if (typeof opts.complete === 'function') {
const helpers = { chalk, logger, files }
opts.complete(data, helpers)
} else {
logMessage(opts.completeMessage, data)
}
})
return data
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
我们将这段代码分为以下部分来讲:
# getOptions
根据这语以化的函数名就知道这是获取配置的,然后详细看下 getOptions 函数的代码:
module.exports = function options (name, dir) {
const opts = getMetadata(dir) // 获取 meta.js 里面的信息,比如:prompts,helpers,filters 等等
setDefault(opts, 'name', name) // 将 meta.js 里面 prompts 字段添加到 inquirer 中,完成命令行的交互
setValidateName(opts) // 检查包的名称是否符合规范
// 获取 name 和 email,用于生成 package.json 里面的 author 字段
const author = getGitUser() // git config --get user.name , git config --get user.email
if (author) {
setDefault(opts, 'author', author)
}
return opts
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
setValidateName 的作用就是利用 validate-npm-package-name (opens new window) 检查你输入的 app-name 是否符合 npm 包名命名规范,当然你也可以在 meta.js 中的 prompts 字段中的 name 下面增加 validate 字段来进行校验,但和 validate-npm-package-name 的规则是 && 的关系。比如,当你输入的 app-name 包含了大写字母,就会有以下的提示:
# Handlebars.registerHelper
Handlebars.registerHelper 用于注册一些 helper(或者说成是一些逻辑方法),在模版中来处理一些数据,比如像源码中注册的 if_eq helper,他的作用就是判断两个字符串是否相等。然后在 webpack 的模板中就有以下的用法:
就是根据你在构建项目时选择的 test runner (Jest,Karma and Mocha,none configure it yourself) 来生成对应的 npm script。你也可以在 meta.js 中添加自定义的 helper,vue-cli 会帮你注册到 Handlebars 中。
# opts.metalsmith
先看一段源码:
if (opts.metalsmith && typeof opts.metalsmith.before === 'function') {
opts.metalsmith.before(metalsmith, opts, helpers)
}
metalsmith.use(askQuestions(opts.prompts))
.use(filterFiles(opts.filters))
.use(renderTemplateFiles(opts.skipInterpolation))
if (typeof opts.metalsmith === 'function') {
opts.metalsmith(metalsmith, opts, helpers)
} else if (opts.metalsmith && typeof opts.metalsmith.after === 'function') {
opts.metalsmith.after(metalsmith, opts, helpers)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
opts.metalsmith 的作用就是合并一些全局变量,怎么理解呢,我们从 webpack 模板入手。在 webpack 模板的 meta.js 中含有metalsmith.after:
module.exports = {
metalsmith: {
// When running tests for the template, this adds answers for the selected scenario
before: addTestAnswers
}
...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
然后一步一步找到 addTestAnswers:
const scenarios = [
'full',
'full-karma-airbnb',
'minimal'
]
const index = scenarios.indexOf(process.env.VUE_TEMPL_TEST)
const isTest = exports.isTest = index !== -1
const scenario = isTest && require(`./${scenarios[index]}.json`)
exports.addTestAnswers = (metalsmith, options, helpers) => {
Object.assign(
metalsmith.metadata(),
{ isNotTest: !isTest },
isTest ? scenario : {}
)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
metalsmith.before 结果就是将 metalsmith metadata 数据和 isNotTest 合并,如果 isTest 为 ture,还会自动设置 name,description等字段。那么它的作用是什么呢,作用就是为模版添加自动测试脚本,它会将 isNotTest 设置为 false,而通过 inquirer 来提问又会是在 isNotTest 为 true 的情况下才会发生,因此设置了VUE_TEMPL_TEST的值会省略 inquirer 提问过程,并且会根据你设置的值来生成对应的模板,有以下三种值可以设置:
- minimal:这种不会设置 router,eslint 和 tests
- full: 会带有 router,eslint (standard) 和 tests (jest & e2e)
- full-airbnb-karma:带有 router eslint(airbnb) 和 tests(karma)
那么如何使用某一种呢,命令如下:
VUE_TEMPL_TEST=full vue init webpack demo
在这种情况下,会自动跳过 inquirer 的问题,并生成你设置的 VUE_TEMPL_TEST。
# metalsmith.use
metalsmith.use 是 metalsmith 使用插件的写法,前面说过 metalsmith 最大的特点就是所有的逻辑都是由插件处理,在 generate 函数中一共有使用了三个 metalsmith 插件,分别为:askQuestions filterFiles renderTemplateFiles 。
- askQuestions
function askQuestions (prompts) {
return (files, metalsmith, done) => {
ask(prompts, metalsmith.metadata(), done)
}
}
2
3
4
5
ask 函数又是独立出来的一个模块,源码(主要代码)为:
// ...
module.exports = function ask (prompts, data, done) {
async.eachSeries(Object.keys(prompts), (key, next) => {
prompt(data, key, prompts[key], next)
}, done)
}
function prompt (data, key, prompt, done) {
// skip prompts whose when condition is not met
if (prompt.when && !evaluate(prompt.when, data)) {
return done()
}
let promptDefault = prompt.default
if (typeof prompt.default === 'function') {
promptDefault = function () {
return prompt.default.bind(this)(data)
}
}
inquirer.prompt([{
type: promptMapping[prompt.type] || prompt.type,
name: key,
message: prompt.message || prompt.label || key,
default: promptDefault,
choices: prompt.choices || [],
validate: prompt.validate || (() => true)
}]).then(answers => {
if (Array.isArray(answers[key])) {
data[key] = {}
answers[key].forEach(multiChoiceAnswer => {
data[key][multiChoiceAnswer] = true
})
} else if (typeof answers[key] === 'string') {
data[key] = answers[key].replace(/"/g, '\\"')
} else {
data[key] = answers[key]
}
done()
}).catch(done)
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
根据这个语以话的命令以及看一些 ask 函数的实现,就明白这个 askQuestions 就是通过 inquirer.prompt 来实现命令行交互,并将交互的值通过 metalsmith.metadata() 存到全局,然后在渲染模板的时候直接获取这些值。
- filterFiles
function filterFiles (filters) {
return (files, metalsmith, done) => {
filter(files, filters, metalsmith.metadata(), done)
}
}
2
3
4
5
filter 函数也是独立出来的一个模块,源码(主要代码)如下:
module.exports = (files, filters, data, done) => {
if (!filters) {
return done()
}
const fileNames = Object.keys(files)
Object.keys(filters).forEach(glob => {
fileNames.forEach(file => {
if (match(file, glob, { dot: true })) { // ~/.vue-templates 下面如果有文件名和 filters下的某一个字段匹配上
const condition = filters[glob]
if (!evaluate(condition, data)) { // 如果 metalsmith.metadata()下 condition 表达式不成立,删除该文件
delete files[file]
}
}
})
})
done()
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
大致描述以下这个过程: meta.js 中 filter 字段如下:
filters: {
'.eslintrc.js': 'lint',
'.eslintignore': 'lint',
'config/test.env.js': 'unit || e2e',
'build/webpack.test.conf.js': "unit && runner === 'karma'",
'test/unit/**/*': 'unit',
'test/unit/index.js': "unit && runner === 'karma'",
'test/unit/jest.conf.js': "unit && runner === 'jest'",
'test/unit/karma.conf.js': "unit && runner === 'karma'",
'test/unit/specs/index.js': "unit && runner === 'karma'",
'test/unit/setup.js': "unit && runner === 'jest'",
'test/e2e/**/*': 'e2e',
'src/router/**/*': 'router',
},
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
一看应该就大致知道是什么意思。以 .eslintrc.js 为例,在模板中默认是有 .eslintrc.js 文件的。利用 vue-cli 初始化一个项目的时候,会询问你 Use ESLint to lint your code? ,然后 inquirer.prompt 通过回调将你回答的值存在 metalsmith.metadata() 的 lint 字段中,在调用 filter 方法的时候就会通过 evaluate 函数来判断在 metalsmith.metadata() 下 lint 的值是否为 true,如果为 false 的就会删除 .eslintrc.js。
- renderTemplateFiles
renderTemplateFiles 源码如下
function renderTemplateFiles (skipInterpolation) {
// 在 meta.js 的 skipInterpolation 下面添加跳过插值的文件,这样在渲染的时候就不会使用 consolidate.handlebars.render 去渲染页面
skipInterpolation = typeof skipInterpolation === 'string'
? [skipInterpolation]
: skipInterpolation
return (files, metalsmith, done) => {
const keys = Object.keys(files)
const metalsmithMetadata = metalsmith.metadata()
async.each(keys, (file, next) => {
// skipping files with skipInterpolation option
if (skipInterpolation && multimatch([file], skipInterpolation, { dot: true }).length) {
return next()
}
const str = files[file].contents.toString()
// do not attempt to render files that do not have mustaches
// 如果在该文件中没有遇到 {{}} (小胡子)就跳过该文件
if (!/{{([^{}]+)}}/g.test(str)) {
return next()
}
render(str, metalsmithMetadata, (err, res) => {
if (err) {
err.message = `[${file}] ${err.message}`
return next(err)
}
files[file].contents = new Buffer(res)
next()
})
}, done)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
renderTemplateFiles 的主要功能就是利用 consolidate.handlebars.render 将 ~/.vue-templates下面的 handlebars 模板文件渲染成正式的文件。
# metalsmith.build
metalsmith.build 就是使用刚才分析的 askQuestions 、filterFiles 和 renderTemplateFiles 三个插件将项目的初始化文件生成出来并输出到目标目录,完成后输出相关的信息。
generate 函数分析就到此为止,在下一节会通过一张流程图来总结整个 vue init 命令的过程。
# 总结
通过一张图来回顾 vue init 命令:
从这个图可以比较清晰地看出 vue init 命令的整个流程,分析源码也是一样,跟着代码的执行顺序一步一步地分析,从而可以将整个流程搞清。虽然在 vue-cli 3.0 当中 vue init 是一个遗留的 API,不推荐使用,但是通过 vue init 来了解 node 命令行脚手架工具搭建还是一个不错的选择。
# vue config
# config 命令
源码目录: packages/@vue/cli/lib/config.js 。
作用: 审查或修改全局的 CLI 配置 。
vue config 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js 中:
program
.command('config [value]')
.description('inspect and modify the config')
.option('-g, --get <path>', 'get value from option')
.option('-s, --set <path> <value>', 'set option value')
.option('-d, --delete <path>', 'delete option from config')
.option('-e, --edit', 'open config with default editor')
.option('--json', 'outputs JSON result only')
.action((value, cmd) => {
require('../lib/config')(value, cleanArgs(cmd))
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
vue config 参数比较好理解,注意一下的就是 <path> 这个值,它用于指定特定配置的路径,比如想要查看 .vuerc 中 presets 的值,可使用以下命令:
vue config -g presets
如果想要查看某一个 preset 的详细信息,例如查看名称为 demo 的 preset,config 命令如下:
vue config -g presets.demo
path 就是一个路径,一级一级地查找,以 . 分割,接下来分析下 config.js 的内容。
module.exports = (...args) => {
return config(...args).catch(err => {
error(err)
if (!process.env.VUE_CLI_TEST) {
process.exit(1)
}
})
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
当执行 vue config 命令时,执行了 config 函数,接着看 config 函数内容:
async function config (value, options) {
const file = path.resolve(homedir, '.vuerc') // 获取 .vuerc 路径
const config = await fs.readJson(file) // 获取 .vuerc 中的内容
if (!options.delete && !options.get && !options.edit && !options.set) { // 输出 .vuerc 内容
if (options.json) { // --json
console.log(JSON.stringify({
resolvedPath: file,
content: config
}))
} else {
console.log('Resolved path: ' + file + '\n', JSON.stringify(config, null, 2))
}
}
if (options.get) { // 获取 .vuerc 中某个指定的配置,vue config -g presets 可以获取预设的值
const value = get(config, options.get)
if (options.json) {
console.log(JSON.stringify({
value
}))
} else {
console.log(value)
}
}
if (options.delete) { // 删除 .vuerc 中某个指定的配置
unset(config, options.delete)
await fs.writeFile(file, JSON.stringify(config, null, 2), 'utf-8')
if (options.json) {
console.log(JSON.stringify({
deleted: options.delete
}))
} else {
console.log(`You have removed the option: ${options.delete}`)
}
}
if (options.edit) { // 启用编辑器编辑 .vuerc
launch(file)
}
if (options.set && !value) {
throw new Error(`Make sure you define a value for the option ${options.set}`)
}
if (options.set && value) { // 设置 config,做一些类型处理
set(config, options.set, value)
if (value.match('[0-9]')) {
set(config, options.set, parseInt(value))
}
if (value === 'true') {
set(config, options.set, true)
}
if (value === 'false') {
set(config, options.set, false)
}
await fs.writeFile(file, JSON.stringify(config, null, 2), 'utf-8')
if (options.json) {
console.log(JSON.stringify({
updated: options.set
}))
} else {
console.log(`You have updated the option: ${options.set} to ${value}`)
}
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
首先读取了 .vuerc 内容,然后根据参数处理对应的情形,下面以 --get <path> 为例来分析,处理 get 情形的代码如下:
if (options.get) { // 获取 .vuerc 中某个指定的配置,vue config -g presets 可以获取预设的值
const value = get(config, options.get)
if (options.json) {
console.log(JSON.stringify({
value
}))
} else {
console.log(value)
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
获取 value 的任务交给了 @vue/cli-shared-utils 中的 get 函数,那么继续看:
exports.get = function (target, path) {
const fields = path.split('.')
let obj = target
const l = fields.length
for (let i = 0; i < l - 1; i++) {
const key = fields[i]
if (!obj[key]) {
return undefined
}
obj = obj[key]
}
return obj[fields[l - 1]]
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
先将 get 参数值以 . 分割,然后循环一级一级地遍历 obj 对象的值,最后返回。其他 set, delete 与 get 类似,就不做分析了,注意一下的就是 set 命令会对 输入的内容进行一定的处理,因为终端输入的内容都是 String 类型,因此检测到含有数字,则将其转为 Number 类型,如果检测到 'true' || 'false',会将其转为 Boolean 类型。
# vue upgrade
# upgrade 命令
源码目录: packages/@vue/cli-upgrade 。
作用: 升级 @vue/cli-service 和 vue-cli 插件。
vue upgrade 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js 中:
program
.command('upgrade [semverLevel]')
.description('upgrade vue cli service / plugins (default semverLevel: minor)')
.action((semverLevel, cmd) => {
loadCommand('upgrade', '@vue/cli-upgrade')(semverLevel, cleanArgs(cmd))
})
2
3
4
5
6
代码比较少,需要注意的就是 semverLevel,它用于指定安装 @vue/cli-service || @vue/cli-plugin-* 的版本号形式,可选择值有三个,默认值为 minor:
- patch: 升级到最新补丁版号
- minor: 升级到最新次版本号
- major: 升级到最新主版本号
先看下 @vue/cli-upgrade/index.js 代码,即 upgrade 命令执行的函数:
module.exports = async function vueCliUpgrade (semverLevel = 'minor'){
// get current deps
// filter @vue/cli-service & @vue/cli-plugin-*
const pkg = getPackageJson(projectPath)
const upgradableDepMaps = new Map([
['dependencies', new Map()],
['devDependencies', new Map()],
['optionalDependencies', new Map()]
])
logWithSpinner('Gathering update information...')
for (const depType of upgradableDepMaps.keys()) {
for (const [packageName, currRange] of Object.entries(pkg[depType] || {})) {
if (!isCorePackage(packageName)) {
continue
}
const upgradable = getUpgradableVersion(
packageName,
currRange,
semverLevel
)
if (upgradable !== currRange) {
upgradableDepMaps.get(depType).set(packageName, upgradable)
}
}
}
// some code ...
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
首先获取了项目的 package.json,然后获取其中的 dependencies,devDependencies,optionalDependencies。获取了这些依赖后利用 isCorePackage 过滤掉不是 @vue/cli-service 和 @vue/cli-plugin-* 的依赖,再分别获取过滤后的依赖需要更新到的版本号,获取版本号使用了 getUpgradableVersion 方法:
module.exports = function getUpgradableVersion (
packageName,
currRange,
semverLevel
) {
let newRange
if (semverLevel === 'patch') { // 安装最近的小版本依赖包, 补丁号
const currMaxVersion = getMaxSatisfying(packageName, currRange)
newRange = `~${currMaxVersion}`
const newMaxVersion = getMaxSatisfying(packageName, newRange)
newRange = `~${newMaxVersion}`
} else if (semverLevel === 'minor') { // 安装最近大版本依赖包,次版本号
const currMaxVersion = getMaxSatisfying(packageName, currRange)
newRange = `^${currMaxVersion}`
const newMaxVersion = getMaxSatisfying(packageName, newRange)
newRange = `^${newMaxVersion}`
} else if (semverLevel === 'major') { // 主版本号
newRange = `^${getMaxSatisfying(packageName, 'latest')}`
} else {
throw new Error('Release type must be one of patch | minor | major!')
}
return newRange
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
通过 getMaxSatisfying 方法执行 npm view 命令获取依赖的版本号,然后根据 semverLevel 确定版本号的形式并返回。如果返回的版本号与当前 package.json 里面依赖的不一致,则将需要升级的信息存在 table 中,以便后续利用 cli-table (opens new window) 输出到控制台上,除此之外还将该依赖名称和需要升级的版本号存在 Map 结构中。
在此之后会遍历 upgradableDepMaps,判断依赖是否有更新信息,如果有则输出信息并询问是否需要安装依赖,否则直接退出。
# vue info
# info 命令
源码目录: 主要依赖了 npm 包 envinfo (opens new window)。
作用: 输出环境的调试信息。
vue info 命令的入口在 packages/@vue/cli/bin/vue.js 中:
program
.command('info')
.description('print debugging information about your environment')
.action((cmd) => {
console.log(chalk.bold('\nEnvironment Info:'))
require('envinfo').run(
{
System: ['OS', 'CPU'],
Binaries: ['Node', 'Yarn', 'npm'],
Browsers: ['Chrome', 'Edge', 'Firefox', 'Safari'],
npmPackages: '/**/{*vue*,@vue/*/}',
npmGlobalPackages: ['@vue/cli']
},
{
showNotFound: true,
duplicates: true,
fullTree: true
}
).then(console.log)
})
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
npm info 命令主要利用 npm envinfo 包输出一些环境的调试信息,比如系统信息,二进制执行文件信息,浏览器信息,项目中与 vue 相关的 npm 包的版本号以及全局 @vue/cli 信息,更多关于 envinfo 的使用可查看详细文档envinfo (opens new window)。
# 相关链接
https://kuangpf.com/vue-cli-analysis

